2 Developing a Business Plan
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the purposes for business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- Explain common business plan development guidelines and tools
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process
- Explain the purposes of each element of the business plan development process
- Explain how applying the business plan development process can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
Overview
This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan.
Purposes for Developing Business Plans
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. Externally, the most common purpose is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
As the road map for a business’s development, the business plan
- Defines the vision for the company
- Establishes the company’s strategy
- Describes how the strategy will be implemented
- Provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- Provides a plan for the development of the business
- Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical success factors
- Helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and test theories
External Purposes
The business plan provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business. Thus, it is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel.
Business Plan Development Principles[1]
Hindle and Mainprize suggested that business plan writers must strive to effectively communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future and to project credibility. The liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures much more difficult than for existing businesses. Consequently, business plan writers should adhere to five specific communication principles.
First, business plans must be written to meet the expectations of targeted readers in terms of what they need to know to support the proposed business. They should also lay out the milestones that investors or other targeted readers need to know. Finally, writers must clearly outline the opportunity, the context within the proposed venture will operate (internal and external environment), and the business model.
There are also five business plan credibility principles that writers should consider. Business plan writers should build and establish their credibility by highlighting important and relevant information about the venture team. Writers need to elaborate on the plans they outline in their document so that targeted readers have the information they need to assess the plan’s credibility. To build and establish credibility, they must integrate scenarios to show that the entrepreneur has made realistic assumptions and has effectively anticipated what the future holds for their proposed venture. Writers need to provide comprehensive and realistic financial links between all relevant components of the plan. Finally, they must outline the deal, or the value that targeted readers should expect to derive from their involvement with the venture.[2]
General Guidelines for Developing Business Plans
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. Using a standard format helps the reader understand that the you have thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
As You Write Your Business Plan
- If appropriate, include nice, catchy, professional graphics on your title page to make it appealing to targeted readers, but don’t go overboard.
- Bind your document so readers can go through it easily without it falling apart. You might use a three-ring binder, coil binding, or a similar method. Make sure the binding method you use does not obscure the information next to where it is bound.
- Make certain all of your pages are ordered and numbered correctly.
- The usual business plan convention is to number all major sections and subsections within your plan using the format as follows:
1. First main heading
1.1 First subheading under the first main heading
1.1.1. First sub-subheading under the first subheading
2. Second main heading
2.1 First subheading under the second main heading
Use the styles and references features in Word to automatically number and format your section titles and to generate your table of contents. Be sure that the last thing you do before printing your document is update your automatic numbering and automatically generated tables. If you fail to do this, your numbering may be incorrect.
5. Prior to submitting your plan, be 100% certain each of the following requirements are met:
- Everything must be completely integrated. The written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part.
- All financial statements must be completely linked and valid. Make sure all of your balance sheets balance.
- Everything must be correct. There should be NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors.
- Your document must be well organized and formatted. The layout you choose should make the document easy to read and comprehend. All of your diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions should be easy to find and be located in the parts of the plan best suited to them.
- In some cases it can strengthen your business plan to show some information in both text and table or figure formats. You should avoid unnecessary repetition, however, as it is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once.
- You should include all the information necessary for readers to understand everything in your document.
- The terms you use in your plan should be clear and consistent. For example, the following statement in a business plan would leave a reader completely confused:
“There is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units.”This statement might mean there is a total shortage of 100,000 units, but competitors are filling this gap by producing 25,000 per year; in which case there will only be a shortage for four years. However, it could mean that the annual shortage is 100,000 units and only 25,000 are produced each year, in which case the total shortage is very high and is growing each year.
- You must always provide the complete perspective by indicating the appropriate time frame, currency, size, or other measurement.
- If you use a percentage figure, you must indicate to what it refers—otherwise the number is meaningless to a reader.
- If your plan includes an international element, you must indicate in which currency or currencies the costs, revenues, prices, or other values are quoted. This can be solved by indicating up-front in the document in which currency all values will be quoted. Another option is to indicate each time which currency is being used, and sometimes you might want to indicate the value in more than one currency. Of course, you will need to assess the exchange rate risk to which you will be exposed and describe this in your document.
6. Ensure credibility is both established and maintained.[3]
- If a statement presents something as a fact when this fact is not generally known, always indicate the source. Unsupported statements damage credibility.
- Be specific. A business plan is simply not of value if it uses vague references to high demand, carefully set prices, and other weak phrasing. It must show hard numbers (properly referenced, of course), actual prices, and real data acquired through proper research. This is the only way to ensure your plan is considered credible.
- Your strategies must be integrated. For example, your pricing strategy must complement and mesh perfectly with your product/service strategy, distribution strategy, and promotions strategy. For example, you probably shouldn’t promote your product as a premium product if you plan to charge lower-than-market prices for it.
7. Before finalizing your business plan, re-read each section to evaluate whether it will appeal to your targeted readers.
Useful Resources for Business Planning
- Financial Performance Data: Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada
- BizPal for accessing licensing and other needs
- Canada Revenue Agency for CRA asset classifications
- Canadian Company Capabilities database to use to find suppliers and buyers
- Merx for finding possible Canadian Government contracts
- The Conference Board of Canada
- Bank of Canada
Bank Sites
Library Resources
NSCC Library – Business Databases [journals and other resources]
Employee compensation calculators
Existing business plans
The Word and Excel templates in this book
Business Plan Development Tools
Credibility and Communication
According to Hindle and Mainprize, strong business plans effectively communicate the necessary information to the targeted readers while also establishing the credibility of the plan and the entrepreneur.[4] The Credibility and Communication Meter icon is used throughout this book to highlight where and how business plan writers can improve the quality of the information and enhance their and their plan’s credibility.
| Credibility and Communication Meter |
Use the following tools to improve the information in and credibility of your plans:
The Ratchet Effect
A ratchet is a tool that most of us are familiar with. It is useful because it helps its user accomplish something with each effort expended while guarding against losing past advancements.
With each word, sentence, paragraph, heading, chart, figure, and table you include in your final business plan, the ratchet should move ahead a notch because you achieve two important things.
First, only needed and relevant information is included.
Second, your additions build credibility in a relevant way.
Apply the ratchet effect by making sure that each and every sentence and paragraph conveys needed and relevant information that adds to your and your plan’s credibility. Use the following principles:
Rarely—and only if it truly needs to be said again—repeat something that you have already said in your plan.
Avoid using killer phrases, like “there is no competition for our product” or “our product will sell itself, so we will not need to advertise it.” Any savvy reader will understand that these kinds of statements are naive and demonstrate a lack of understanding about how the market and other real-life factors actually work.
Avoid contradicting yourself. Make sure that what is said in the written part of your plan completely syncs with what is said in the other parts of your plan. Likewise, ensure that what you include in the financial parts of your plan is completely in sync with what is said the written part.
The Magic Formula
Apply the following magic formula throughout your write your plan.
- …consideration X affects my business because…
- …consideration X is subject to this trend into the future…
- …which means that we have decided to do this…(or) will implement this strategy…in response to how the expected trends for consideration X will affect my business
Here is an example of how you can use the magic formula to develop part of the pricing strategy in the marketing plan part of your business plan:
We expect that our expenses to run our business will rise with the rate of inflation, which means that we must plan to increase the prices on our products to establish and maintain our profitability. The Bank of Canada (201x) has projected that the general inflation rate in <the city in which my business will operate> will be 3.0% in 201x, 3.5% in 201y, and 4.0% in 201z. In our projected financial statements, therefore, we have inflated both our expenses and our prices by those rates in those years.
Context and Framing
You must provide the right context when you describe situations, strategies, and other components of your plan. Business plan readers should never be left to guess why you indicate in a business plan that you will do something. Proper context is needed to help you frame the information you present.
When you frame the stories you tell correctly, the ratchet effect will happen and your plan will be stronger. One example of effective framing is when you, as the writer of the plan and the entrepreneur, clearly indicate how your education, expertise, relevant experiences, and network of contacts will make up for any lack of direct experience you have in running this particular kind of business. An example of ineffective framing is when you indicate that you lack experience with this type of business, or when you fail to specify how and why your levels of experience will affect the business’s development.
Prioritizing Problems
Don’t get hung up on something that doesn’t need an immediate solution. Instead, flag it for future consideration and move on. When you return to re-address the issue, it might no longer be a problem or you might have by then figured out a solution.
Process for Developing Business Plans
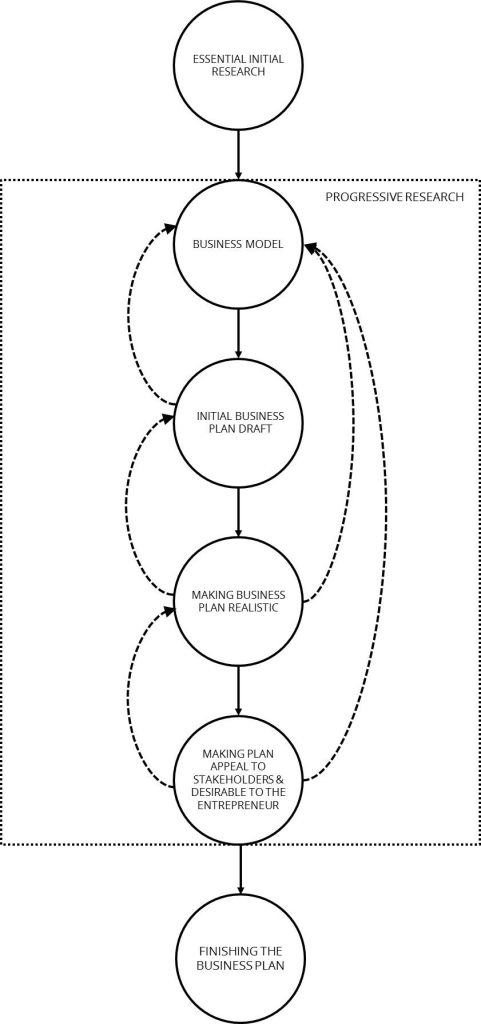
The business plan development process described next has been extensively tested with entrepreneurship students and has proven to provide the guidance entrepreneurs need to develop a business plan appropriate for their needs: a high power business plan.
Developing a high power business plan has six stages, which can be compared to a process for hosting a dinner for a few friends. A host hoping to make a good impression with their anticipated guests might analyze the situation at multiple levels to collect data on new alternatives for healthy ingredients, what ingredients have the best prices and are most readily available at certain times of year, the new trends in party appetizers, what food allergies the expected guests might have, possible party themes, and so on. This analysis is the Essential Initial Research stage.
In the Business Model stage, the host might construct a menu of items to include with the meal along with a list of decorations to order, music to play, and costume themes to suggest to the guests. The mix of these kinds of elements chosen by the host will aid in the success of the party.
The Initial Business Plan Draft stage is where the host rolls up their sleeves and begins to make some of the food items, puts up some of the decorations, and generally gets everything started for the party.
During this stage, the host will begin to realize that some plans are not feasible and that changes are needed. The required changes might be substantial, like the need to postpone the entire party and ultimately start over in a few months, and others might be less drastic, like the need to change the menu when an invited guest indicates that they can’t eat food containing gluten. These changes are incorporated into the plan during the Making the Business Plan Realistic stage to make it realistic and feasible.
The Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur stage involves further changes to the party plan to make it more appealing to both the invited guests and to make it a fun experience for the host. For example, the host might learn that some of the single guests would like to bring dates and others might need to be able to bring their children to be able to attend. The host might be able to accommodate those desires or needs in ways that will also make the party more fun for them—maybe by accepting some guests’ offers to bring food or games, or maybe hiring a babysitter to entertain and look after the children.
The final stage—Finishing the Business Plan—involves the host putting all of the final touches in place for the party in preparation for the arrival of the guests.
Essential Initial Research
A business plan writer should analyze the environment in which they anticipate operating at each of the levels of analysis: Societal, Industry, Market, and Firm. This stage of planning is called the Essential Initial Research stage, and it is a necessary first step to better understand the trends that will affect their business and the decisions they must make to lay the groundwork for, which will improve their potential for success.
In some cases, much of this research should be included in the developing business plan as its own separate section to help show readers that there is a market need for the business being considered and that it stands a good chance of being successful.
In other cases, a business plan will be stronger when the components of the research are distributed throughout the business plan to provide support for the outlined plans and strategies outlined. For example, the industry- or market-level research might outline the pricing strategies used by identified competitors, which might be best placed in the Pricing Strategy part of the business plan to support the decision made to employ a particular pricing strategy.
Business Model
Inherent in any business plan is a description of the Business Model chosen by the entrepreneur as the one that they feel will best ensure success. Based upon their analysis from the Essential Initial Research stage, an entrepreneur should determine how each element of their business model—including their revenue streams, cost structure, customer segments, value propositions, key activities, key partners, and so on—might fit together to improve the potential success of their business venture (see Chapter 3 – Business Models).
For some types of ventures, at this stage an entrepreneur might launch a lean start-up (see the “Lean Start-up” section in Chapter 2 – Essential Initial Research) and grow their business by continually pivoting, or constantly adjusting their business model in response to the real-time signals they get from the markets’ reactions to their business operations. In many cases, however, an entrepreneur will require a business plan. In those cases, their initial business model will provide the basis for that plan.
Of course, throughout this and all of the stages in this process, the entrepreneur should seek to continually gather information and adjust the plans in response to the new knowledge they gather. As shown in Figure 1 by its enclosure in the Progressive Research box, the business plan developer might need to conduct further research before finishing the business model and moving on to the initial business plan draft.
Initial Business Plan Draft
The Initial Business Plan Draft stage involves taking the knowledge and ideas developed during the first two stages and organizing them into a business plan format. Many entrepreneurs prefer to create a full draft of the business plan with all of the sections, including the front part with the business description, vision, mission, values, value proposition statement, preliminary set of goals, and possibly even a table of contents and lists of tables and figures all set up using the software features enabling their automatic generation. Writing all of the operations, human resources, marketing, and financial plans as part of the first draft ensures that all of these parts can be appropriately and necessarily integrated. The business plan will tell the story of a planned business startup in two ways: 1) by using primarily words along with some charts and graphs in the operations, human resources, and marketing plans and 2) through the financial plan. Both must tell the same story.
The feedback loop shown in Figure 1 demonstrates that the business developer may need to review the business model. Additionally, as shown by its enclosure in the Progressive Research box, the business plan developer might need to conduct further research before finishing the Initial Business Plan Draft stage and moving on to the Making Business Plan Realistic stage.
Making Business Plan Realistic
The first draft of a business plan will almost never be realistic. As the entrepreneur writes the plan, it will necessarily change as new information is gathered. Another factor that usually renders the first draft unrealistic is the difficulty in making certain that the written part—in the front part of the plan along with the operations, human resources, and marketing plans—tells the exact same story as the financial part does. This stage of work involves making the necessary adjustments to the plan to make it as realistic as possible.
The Making Business Plan Realistic stage has two possible feedback loops. The first means going back to the Initial Business Plan Draft stage if the initial business plan needs to be significantly changed before it is possible to adjust it so that it is realistic. The second feedback loop circles back to the Business Model stage if the business developer needs to rethink the business model. As shown in Figure 1 by its enclosure in the Progressive Research box, the business plan developer might need to conduct further research before finishing the Making Business Plan Realistic stage and moving on to the Making Plan Appeal to Stakeholders stage.
Making Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
A business plan can be realistic without appealing to potential investors and other external stakeholders, like employees, suppliers, and needed business partners. It might also be realistic (and possibly appealing to stakeholders) without being desirable to the entrepreneur. During this stage, the entrepreneur will keep the business plan realistic as they adjust plans to appeal to potential investors, stakeholders, and themselves.
If, for example, investors will be required to finance the business’s start, some adjustments might need to be relatively extensive to appeal to potential investors’ needs for an exit strategy from the business, to accommodate the rate of return they expect from their investments, and to convince them that the entrepreneur can accomplish all that is promised in the plan. In this case, and in others, the entrepreneur will also need to get what they want out of the business to make it worthwhile for them to start and run it. So, this stage of adjustments to the developing business plan might be fairly extensive, and they must be informed by a superior knowledge of what targeted investors need from a business proposal before they will invest. They also need to be informed by a clear set of goals that will make the venture worthwhile for the entrepreneur to pursue.
The caution with this stage is to balance the need to make realistic plans with the desire to meet the entrepreneur’s goals while avoiding becoming discouraged enough to drop the idea of pursuing the business idea. If an entrepreneur is convinced that the proposed venture will satisfy a valid market need, there is often a way to assemble the financing required to start and operate the business while also meeting the entrepreneur’s most important goals. To do so, however, might require significant changes to the business model.
One of the feedback loops shown in Figure 1 indicates that the business plan writer might need to adjust the draft business plan while ensuring that it is still realistic before it can be made appealing to the targeted stakeholders and desirable to the entrepreneur. The second feedback loop indicates that it might be necessary to go all the way back to the Business Model stage to re-establish the framework and plans needed to develop a realistic, appealing, and desirable business plan. Additionally, this stage’s enclosure in the Progressive Research box suggests that the business plan developer might need to conduct further research.
Finishing the Business Plan
The final stage involves putting the important finishing touches on the business plan so that it will present well to potential investors and others. This involves making sure that the math and links between the written and financial parts are accurate. It involves ensuring that all the needed corrections are made to the spelling, grammar, and formatting. The final set of goals should be written to appeal to the target readers and to reflect what the business plan says. An executive summary should be written and included as a final step.
Chapter Summary
This chapter described the internal and external purposes for business planning. It also explained how business plans must effectively communicate while establishing and building credibility for both the entrepreneur and the venture. The general guidelines for business planning were covered as were some important business planning tools. The chapter concluded with descriptions of the stages of the business development process for effective business planning.

