Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain the processes of digestion and absorption
- Explain the specialized functions of the organs involved in processing food in the body
- Describe the ways in which organs work together to digest food and absorb nutrients
- Describe the essential nutrients required for cellular function that cannot be synthesized by the animal body
- Describe how excess carbohydrates and energy are stored in the body
All living organisms need nutrients to survive. While plants can obtain nutrients from their roots and the energy molecules required for cellular function through the process of photosynthesis, animals obtain their nutrients by the consumption of other organisms. At the cellular level, the biological molecules necessary for animal function are amino acids, lipid molecules, nucleotides, and simple sugars. However, the food consumed consists of protein, fat, and complex carbohydrates. Animals must convert these macromolecules into the simple molecules required for maintaining cellular function. The conversion of the food consumed to the nutrients required is a multistep process involving digestion and absorption. During digestion, food particles are broken down to smaller components, which are later absorbed by the body. This happens by both physical means, such as chewing, and by chemical means.
One of the challenges in human nutrition is maintaining a balance between food intake, storage, and energy expenditure. Taking in more food energy than is used in activity leads to storage of the excess in the form of fat deposits. The rise in obesity and the resulting diseases like type 2 diabetes makes understanding the role of diet and nutrition in maintaining good health all the more important.
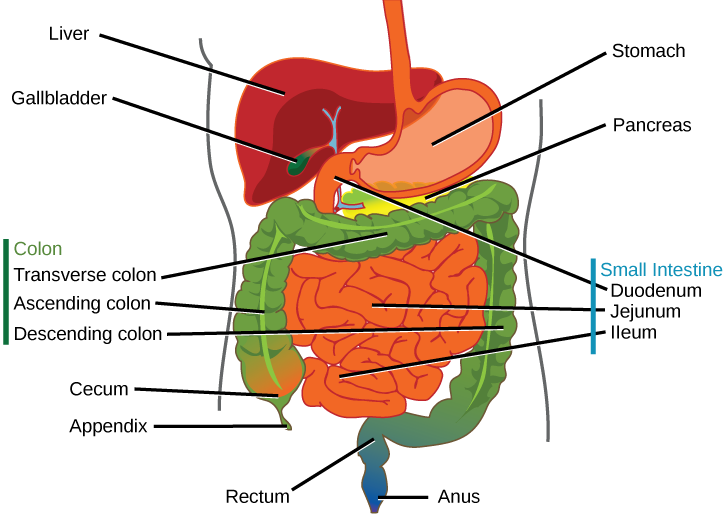
The Human Digestive System
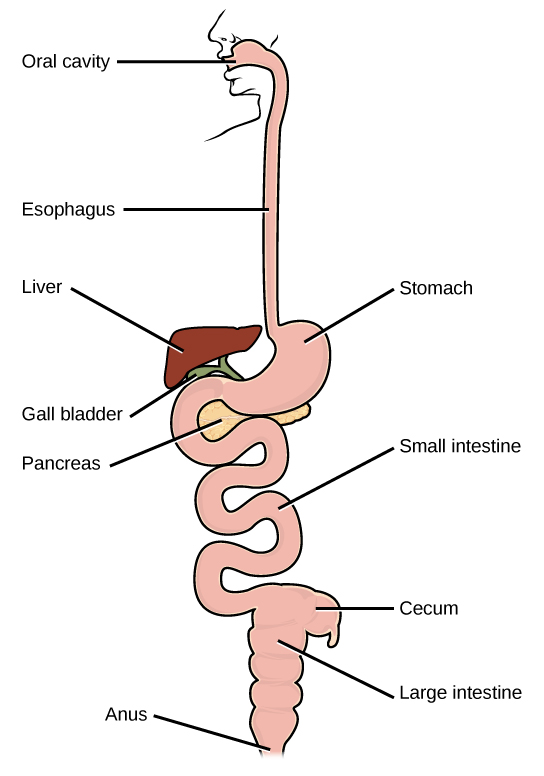
The process of digestion begins in the mouth with the intake of food. The teeth play an important role in masticating (chewing) or physically breaking food into smaller particles. The enzymes present in saliva also begin to chemically break down food. The food is then swallowed and enters the esophagus—a long tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Using peristalsis, or wave-like smooth-muscle contractions, the muscles of the esophagus push the food toward the stomach. The stomach contents are extremely acidic, with a pH between 1.5 and 2.5. This acidity kills microorganisms, breaks down food tissues, and activates digestive enzymes. Further breakdown of food takes place in the small intestine where bile produced by the liver, and enzymes produced by the small intestine and the pancreas, continue the process of digestion. The smaller molecules are absorbed into the blood stream through the epithelial cells lining the walls of the small intestine. The waste material travels on to the large intestine where water is absorbed and the drier waste material is compacted into feces; it is stored until it is excreted through the anus.
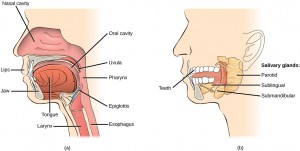
Oral Cavity
Both physical and chemical digestion begin in the mouth or oral cavity, which is the point of entry of food into the digestive system. The food is broken into smaller particles by mastication, the chewing action of the teeth. All mammals have teeth and can chew their food to begin the process of physically breaking it down into smaller particles.
The chemical process of digestion begins during chewing as food mixes with saliva, produced by the salivary glands (Figure 11.5). Saliva contains mucus that moistens food and buffers the pH of the food. Saliva also contains lysozyme, which has antibacterial action. It also contains an enzyme called salivary amylase that begins the process of converting starches in the food into a disaccharide called maltose. Another enzyme called lipase is produced by cells in the tongue to break down fats. The chewing and wetting action provided by the teeth and saliva prepare the food into a mass called the bolus for swallowing. The tongue helps in swallowing—moving the bolus from the mouth into the pharynx. The pharynx opens to two passageways: the esophagus and the trachea. The esophagus leads to the stomach and the trachea leads to the lungs. The epiglottis is a flap of tissue that covers the tracheal opening during swallowing to prevent food from entering the lungs.
Esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular organ that connects the mouth to the stomach. The chewed and softened food passes through the esophagus after being swallowed. The smooth muscles of the esophagus undergo peristalsis that pushes the food toward the stomach. The peristaltic wave is unidirectional—it moves food from the mouth to the stomach, and reverse movement is not possible, except in the case of the vomit reflex. The peristaltic movement of the esophagus is an involuntary reflex; it takes place in response to the act of swallowing.
Ring-like muscles called sphincters form valves in the digestive system. The gastro-esophageal sphincter (or cardiac sphincter) is located at the stomach end of the esophagus. In response to swallowing and the pressure exerted by the bolus of food, this sphincter opens, and the bolus enters the stomach. When there is no swallowing action, this sphincter is shut and prevents the contents of the stomach from traveling up the esophagus. Acid reflux or “heartburn” occurs when the acidic digestive juices escape into the esophagus.
Stomach
A large part of protein digestion occurs in the stomach (Figure 11.7). The stomach is a saclike organ that secretes gastric digestive juices.
Protein digestion is carried out by an enzyme called pepsin in the stomach chamber. The highly acidic environment kills many microorganisms in the food and, combined with the action of the enzyme pepsin, results in the catabolism of protein in the food. Chemical digestion is facilitated by the churning action of the stomach caused by contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles. The partially digested food and gastric juice mixture is called chyme. Gastric emptying occurs within two to six hours after a meal. Only a small amount of chyme is released into the small intestine at a time. The movement of chyme from the stomach into the small intestine is regulated by hormones, stomach distension and muscular reflexes that influence the pyloric sphincter.
The stomach lining is unaffected by pepsin and the acidity because pepsin is released in an inactive form and the stomach has a thick mucus lining that protects the underlying tissue.
Small Intestine
Chyme moves from the stomach to the small intestine. The small intestine is the organ where the digestion of protein, fats, and carbohydrates is completed. The small intestine is a long tube-like organ with a highly folded surface containing finger-like projections called the villi. The top surface of each villus has many microscopic projections called microvilli. The epithelial cells of these structures absorb nutrients from the digested food and release them to the bloodstream on the other side. The villi and microvilli, with their many folds, increase the surface area of the small intestine and increase absorption efficiency of the nutrients.
The human small intestine is over 6 m (19.6 ft) long and is divided into three parts: the duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum. The duodenum is separated from the stomach by the pyloric sphincter. The chyme is mixed with pancreatic juices, an alkaline solution rich in bicarbonate that neutralizes the acidity of chyme from the stomach. Pancreatic juices contain several digestive enzymes that break down starches, disaccharides, proteins, and fats. Bile is produced in the liver and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder; it enters the duodenum through the bile duct. Bile contains bile salts, which make lipids accessible to the water-soluble enzymes. The monosaccharides, amino acids, bile salts, vitamins, and other nutrients are absorbed by the cells of the intestinal lining.
The undigested food is sent to the colon from the ileum via peristaltic movements. The ileum ends and the large intestine begins at the ileocecal valve. The vermiform, “worm-like,” appendix is located at the ileocecal valve. The appendix of humans has a minor role in immunity.
Large Intestine
The large intestine reabsorbs the water from indigestible food material and processes the waste material (Figure 11.6). The human large intestine is much smaller in length compared to the small intestine but larger in diameter. It has three parts: the cecum, the colon, and the rectum. The cecum joins the ileum to the colon and is the receiving pouch for the waste matter. The colon is home to many bacteria or “intestinal flora” that aid in the digestive processes. The colon has four regions, the ascending colon, the transverse colon, the descending colon and the sigmoid colon. The main functions of the colon are to extract the water and mineral salts from undigested food, and to store waste material.
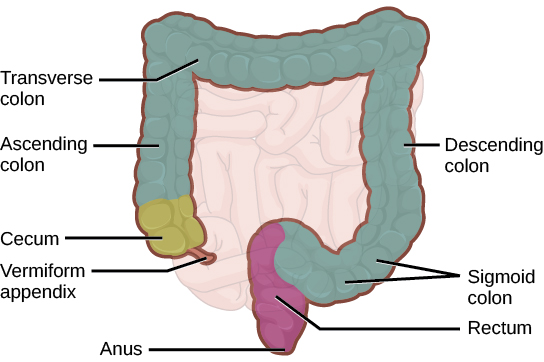
The rectum (Figure 11.6) stores feces until defecation. The feces are propelled using peristaltic movements during elimination. The anus is an opening at the far-end of the digestive tract and is the exit point for the waste material. Two sphincters regulate the exit of feces, the inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer sphincter is voluntary.
Accessory Organs
The organs discussed above are the organs of the digestive tract through which food passes. Accessory organs add secretions and enzymes that break down food into nutrients. Accessory organs include the salivary glands, the liver, the pancreas, and the gall bladder. The secretions of the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder are regulated by hormones in response to food consumption.
The liver is the largest internal organ in humans and it plays an important role in digestion of fats and detoxifying blood. The liver produces bile, a digestive juice that is required for the breakdown of fats in the duodenum. The liver also processes the absorbed vitamins and fatty acids and synthesizes many plasma proteins. The gallbladder is a small organ that aids the liver by storing bile and concentrating bile salts.
The pancreas secretes bicarbonate that neutralizes the acidic chyme and a variety of enzymes for the digestion of protein and carbohydrates.
Nutrition
The following video is primarily about water soluble vitamins such as vitamin B and C their roles, especially in energy metabolism. Some of the more common and obscure minerals found in vitamins are also identified.
Vitamin Types
And the next video is an introduction to another category of vitamins, the fat soluble group such as vitamin E, D and K.
Fat Soluble Vitamins
The human diet should be well balanced to provide nutrients required for bodily function and the minerals and vitamins required for maintaining structure and regulation necessary for good health and reproductive capability (Figure 11.8).

Concept in Action

Explore this interactive United States Department of Agriculture website to learn more about each food group and the recommended daily amounts.
The organic molecules required for building cellular material and tissues must come from food. During digestion, digestible carbohydrates are ultimately broken down into glucose and used to provide energy within the cells of the body. Complex carbohydrates, including polysaccharides, can be broken down into glucose through biochemical modification; however, humans do not produce the enzyme necessary to digest cellulose (fiber). The intestinal flora in the human gut are able to extract some nutrition from these plant fibers. These plant fibers are known as dietary fiber and are an important component of the diet. The excess sugars in the body are converted into glycogen and stored for later use in the liver and muscle tissue. Glycogen stores are used to fuel prolonged exertions, such as long-distance running, and to provide energy during food shortage. Fats are stored under the skin of mammals for insulation and energy reserves.
Proteins in food are broken down during digestion and the resulting amino acids are absorbed. All of the proteins in the body must be formed from these amino-acid constituents; no proteins are obtained directly from food.
Fats add flavor to food and promote a sense of satiety or fullness. Fatty foods are also significant sources of energy, and fatty acids are required for the construction of lipid membranes. Fats are also required in the diet to aid the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and the production of fat-soluble hormones.
While the animal body can synthesize many of the molecules required for function from precursors, there are some nutrients that must be obtained from food. These nutrients are termed essential nutrients, meaning they must be eaten, because the body cannot produce them.
The fatty acids omega-3 alpha-linolenic acid and omega-6 linoleic acid are essential fatty acids needed to make some membrane phospholipids. Vitamins are another class of essential organic molecules that are required in small quantities. Many of these assist enzymes in their function and, for this reason, are called coenzymes. Absence or low levels of vitamins can have a dramatic effect on health. Minerals are another set of inorganic essential nutrients that must be obtained from food. Minerals perform many functions, from muscle and nerve function, to acting as enzyme cofactors. Certain amino acids also must be procured from food and cannot be synthesized by the body. These amino acids are the “essential” amino acids. The human body can synthesize only 11 of the 20 required amino acids; the rest must be obtained from food.
Obesity
With obesity at high rates in the United States, there is a public health focus on reducing obesity and associated health risks, which include diabetes, colon and breast cancer, and cardiovascular disease. How does the food consumed contribute to obesity?
Fatty foods are calorie-dense, meaning that they have more calories per unit mass than carbohydrates or proteins. One gram of carbohydrates has four calories, one gram of protein has four calories, and one gram of fat has nine calories. Animals tend to seek lipid-rich food for their higher energy content. Greater amounts of food energy taken in than the body’s requirements will result in storage of the excess in fat deposits.
Excess carbohydrate is used by the liver to synthesize glycogen. When glycogen stores are full, additional glucose is converted into fatty acids. These fatty acids are stored in adipose tissue cells—the fat cells in the mammalian body whose primary role is to store fat for later use.
The rate of obesity among children is rapidly rising in the United States. To combat childhood obesity and ensure that children get a healthy start in life, in 2010 First Lady Michelle Obama launched the Let’s Move! campaign. The goal of this campaign is to educate parents and caregivers on providing healthy nutrition and encouraging active lifestyles in future generations. This program aims to involve the entire community, including parents, teachers, and healthcare providers to ensure that children have access to healthy foods—more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains—and consume fewer calories from processed foods. Another goal is to ensure that children get physical activity. With the increase in television viewing and stationary pursuits such as video games, sedentary lifestyles have become the norm. Visit www.letsmove.gov to learn more.
Section Summary
There are many organs that work together to digest food and absorb nutrients. The mouth is the point of ingestion and the location where both mechanical and chemical breakdown of food begins. Saliva contains an enzyme called amylase that breaks down carbohydrates. The food bolus travels through the esophagus by peristaltic movements to the stomach. The stomach has an extremely acidic environment. The enzyme pepsin digests protein in the stomach. Further digestion and absorption take place in the small intestine. The large intestine reabsorbs water from the undigested food and stores waste until elimination.
Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the primary components of food. Some essential nutrients are required for cellular function but cannot be produced by the animal body. These include vitamins, minerals, some fatty acids, and some amino acids. Food intake in more than necessary amounts is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscle cells, and in adipose tissue. Excess adipose storage can lead to obesity and serious health problems.