Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- List the different types of hormones and explain their roles in maintaining homeostasis
- Explain how hormones work
- Explain how hormone production is regulated
- Describe the role of different glands in the endocrine system
- Explain how the different glands work together to maintain homeostasis
The endocrine system produces hormones that function to control and regulate many different body processes. The endocrine system coordinates with the nervous system to control the functions of the other organ systems. Cells of the endocrine system produce molecular signals called hormones. These cells may compose endocrine glands, may be tissues or may be located in organs or tissues that have functions in addition to hormone production. Hormones circulate throughout the body and stimulate a response in cells that have receptors able to bind with them. The changes brought about in the receiving cells affect the functioning of the organ system to which they belong. Many of the hormones are secreted in response to signals from the nervous system, thus the two systems act in concert to effect changes in the body.
Hormones
Maintaining homeostasis within the body requires the coordination of many different systems and organs. One mechanism of communication between neighboring cells, and between cells and tissues in distant parts of the body, occurs through the release of chemicals called hormones. Hormones are released into body fluids, usually blood, which carries them to their target cells where they elicit a response. The cells that secrete hormones are often located in specific organs, called endocrine glands, and the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones make up the endocrine system. Examples of endocrine organs include the pancreas, which produces the hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate blood-glucose levels, the adrenal glands, which produce hormones such as epinephrine and norepinephrine that regulate responses to stress, and the thyroid gland, which produces thyroid hormones that regulate metabolic rates.
The endocrine glands differ from the exocrine glands. Exocrine glands secrete chemicals through ducts that lead outside the gland (not to the blood). For example, sweat produced by sweat glands is released into ducts that carry sweat to the surface of the skin. The pancreas has both endocrine and exocrine functions because besides releasing hormones into the blood. It also produces digestive juices, which are carried by ducts into the small intestine.
Endocrinologist
An endocrinologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating endocrine disorders. An endocrine surgeon specializes in the surgical treatment of endocrine diseases and glands. Some of the diseases that are managed by endocrinologists include disorders of the pancreas (diabetes mellitus), disorders of the pituitary (gigantism, acromegaly, and pituitary dwarfism), disorders of the thyroid gland (goiter and Graves’ disease), and disorders of the adrenal glands (Cushing’s disease and Addison’s disease).
Endocrinologists are required to assess patients and diagnose endocrine disorders through extensive use of laboratory tests. Many endocrine diseases are diagnosed using tests that stimulate or suppress endocrine organ functioning. Blood samples are then drawn to determine the effect of stimulating or suppressing an endocrine organ on the production of hormones. For example, to diagnose diabetes mellitus, patients are required to fast for 12 to 24 hours. They are then given a sugary drink, which stimulates the pancreas to produce insulin to decrease blood-glucose levels. A blood sample is taken one to two hours after the sugar drink is consumed. If the pancreas is functioning properly, the blood-glucose level will be within a normal range. Another example is the A1C test, which can be performed during blood screening. The A1C test measures average blood-glucose levels over the past two to three months. The A1C test is an indicator of how well blood glucose is being managed over a long time.
Once a disease such as diabetes has been diagnosed, endocrinologists can prescribe lifestyle changes and medications to treat the disease. Some cases of diabetes mellitus can be managed by exercise, weight loss, and a healthy diet; in other cases, medications may be required to enhance insulin’s production or effect. If the disease cannot be controlled by these means, the endocrinologist may prescribe insulin injections.
In addition to clinical practice, endocrinologists may also be involved in primary research and development activities. For example, ongoing islet transplant research is investigating how healthy pancreas islet cells may be transplanted into diabetic patients. Successful islet transplants may allow patients to stop taking insulin injections.
How Hormones Work
Hormones cause changes in target cells by binding to specific cell-surface or intracellular hormone receptors, molecules embedded in the cell membrane or floating in the cytoplasm with a binding site that matches a binding site on the hormone molecule. In this way, even though hormones circulate throughout the body and come into contact with many different cell types, they only affect cells that possess the necessary receptors. Receptors for a specific hormone may be found on or in many different cells or may be limited to a small number of specialized cells. For example, thyroid hormones act on many different tissue types, stimulating metabolic activity throughout the body. Cells can have many receptors for the same hormone but often also possess receptors for different types of hormones. The number of receptors that respond to a hormone determines the cell’s sensitivity to that hormone, and the resulting cellular response. Additionally, the number of receptors available to respond to a hormone can change over time, resulting in increased or decreased cell sensitivity. In up-regulation, the number of receptors increases in response to rising hormone levels, making the cell more sensitive to the hormone and allowing for more cellular activity. When the number of receptors decreases in response to rising hormone levels, called down-regulation, cellular activity is reduced.
Endocrine Glands
The endocrine glands secrete hormones into the surrounding interstitial fluid; those hormones then diffuse into blood and are carried to various organs and tissues within the body. The endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, gonads, pineal, and pancreas.
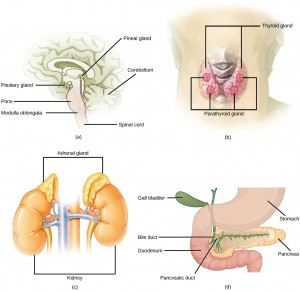
The pituitary gland, sometimes called the hypophysis, is located at the base of the brain (Figure 11.23 a). It is attached to the hypothalamus. The posterior lobe stores and releases oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone produced by the hypothalamus. The anterior lobe responds to hormones produced by the hypothalamus by producing its own hormones, most of which regulate other hormone-producing glands.
The anterior pituitary produces six hormones: growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and luteinizing hormone. Growth hormone stimulates cellular activities like protein synthesis that promote growth. Prolactin stimulates the production of milk by the mammary glands. The other hormones produced by the anterior pituitary regulate the production of hormones by other endocrine tissues (Table 11.1). The posterior pituitary is significantly different in structure from the anterior pituitary. It is a part of the brain, extending down from the hypothalamus, and contains mostly nerve fibers that extend from the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary.
The thyroid gland is located in the neck, just below the larynx and in front of the trachea (Figure 11.23 b). It is a butterfly-shaped gland with two lobes that are connected. The thyroid follicle cells synthesize the hormone thyroxine, which is also known as T4 because it contains four atoms of iodine, and triiodothyronine, also known as T3 because it contains three atoms of iodine. T3 and T4 are released by the thyroid in response to thyroid-stimulating hormone produced by the anterior pituitary, and both T3 and T4 have the effect of stimulating metabolic activity in the body and increasing energy use. A third hormone, calcitonin, is also produced by the thyroid. Calcitonin is released in response to rising calcium ion concentrations in the blood and has the effect of reducing those levels.
Most people have four parathyroid glands; however, the number can vary from two to six. These glands are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland (Figure 11.23 b).
The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone. Parathyroid hormone increases blood calcium concentrations when calcium ion levels fall below normal.
The adrenal glands are located on top of each kidney (Figure 11.23 c). The adrenal glands consist of an outer adrenal cortex and an inner adrenal medulla. These regions secrete different hormones.
The adrenal cortex produces mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. The main mineralocorticoid is aldosterone, which regulates the concentration of ions in urine, sweat, and saliva. Aldosterone release from the adrenal cortex is stimulated by a decrease in blood concentrations of sodium ions, blood volume, or blood pressure, or by an increase in blood potassium levels. The glucocorticoids maintain proper blood-glucose levels between meals. They also control a response to stress by increasing glucose synthesis from fats and proteins and interact with epinephrine to cause vasoconstriction. Androgens are sex hormones that are produced in small amounts by the adrenal cortex. They do not normally affect sexual characteristics and may supplement sex hormones released from the gonads. The adrenal medulla contains two types of secretory cells: one that produces epinephrine (adrenaline) and another that produces norepinephrine (noradrenaline). Epinephrine and norepinephrine cause immediate, short-term changes in response to stressors, inducing the so-called fight-or-flight response. The responses include increased heart rate, breathing rate, cardiac muscle contractions, and blood-glucose levels. They also accelerate the breakdown of glucose in skeletal muscles and stored fats in adipose tissue, and redirect blood flow toward skeletal muscles and away from skin and viscera. The release of epinephrine and norepinephrine is stimulated by neural impulses from the sympathetic nervous system that originate from the hypothalamus.
The pancreas is an elongate organ located between the stomach and the proximal portion of the small intestine (Figure 11.23 d). It contains both exocrine cells that excrete digestive enzymes and endocrine cells that release hormones.
The endocrine cells of the pancreas form clusters called pancreatic islets or the islets of Langerhans. Among the cell types in each pancreatic islet are the alpha cells, which produce the hormone glucagon, and the beta cells, which produce the hormone insulin. These hormones regulate blood-glucose levels. Alpha cells release glucagon as blood-glucose levels decline. When blood-glucose levels rise, beta cells release insulin. Glucagon causes the release of glucose to the blood from the liver, and insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by the body’s cells.
The gonads—the male testes and female ovaries—produce steroid hormones. The testes produce androgens, testosterone being the most prominent, which allow for the development of secondary sex characteristics and the production of sperm cells. The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone, which cause secondary sex characteristics, regulate production of eggs, control pregnancy, and prepare the body for childbirth.
There are several organs whose primary functions are non-endocrine but that also possess endocrine functions. These include the heart, kidneys, intestines, thymus, and adipose tissue. The heart has endocrine cells in the walls of the atria that release a hormone in response to increased blood volume. It causes a reduction in blood volume and blood pressure, and reduces the concentration of Na+ in the blood.
The gastrointestinal tract produces several hormones that aid in digestion. The endocrine cells are located in the mucosa of the GI tract throughout the stomach and small intestine. They trigger the release of gastric juices, which help to break down and digest food in the GI tract.
The kidneys also possess endocrine function. Two of these hormones regulate ion concentrations and blood volume or pressure. Erythropoietin (EPO) is released by kidneys in response to low oxygen levels. EPO triggers the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. EPO has been used by athletes to improve performance. But EPO doping has its risks, since it thickens the blood and increases strain on the heart; it also increases the risk of blood clots and therefore heart attacks and stroke.
The thymus is found behind the sternum. The thymus produces hormones referred to as thymosins, which contribute to the development of the immune response in infants. Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, produces the hormone leptin in response to food intake. Leptin produces a feeling of satiety after eating, reducing the urge for further eating.
| Endocrine Gland | Associated Hormones | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Pituitary (anterior) | growth hormone | promotes growth of body tissues |
| prolactin | promotes milk production | |
| thyroid-stimulating hormone | stimulates thyroid hormone release | |
| adrenocorticotropic hormone | stimulates hormone release by adrenal cortex | |
| follicle-stimulating hormone | stimulates gamete production | |
| luteinizing hormone | stimulates androgen production by gonads in males; stimulates ovulation and production of estrogen and progesterone in females | |
| Pituitary (posterior) | antidiuretic hormone | stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys |
| oxytocin | stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth | |
| Thyroid | thyroxine, triiodothyronine | stimulate metabolism |
| calcitonin | reduces blood Ca2+ levels | |
| Parathyroid | parathyroid hormone | increases blood Ca2+ levels |
| Adrenal (cortex) | aldosterone | increases blood Na+ levels |
| cortisol, corticosterone, cortisone | increase blood-glucose levels | |
| Adrenal (medulla) | epinephrine, norepinephrine | stimulate fight-or-flight response |
| Pancreas | insulin | reduces blood-glucose levels |
| glucagon | increases blood-glucose levels |
Regulation of Hormone Production
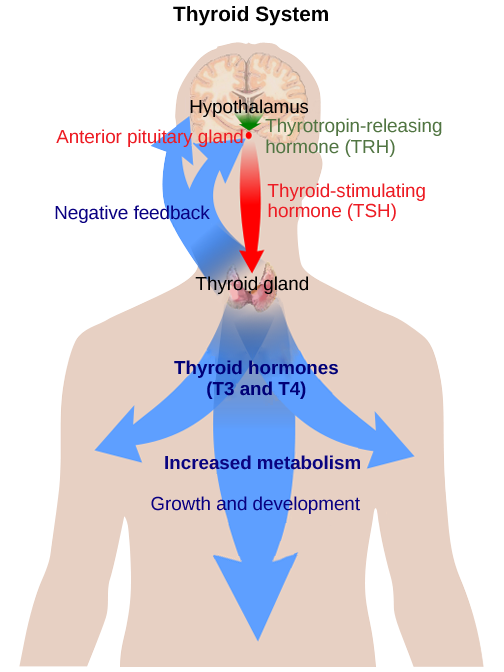
Hormone production and release are primarily controlled by negative feedback, as described in the discussion on homeostasis. In this way, the concentration of hormones in blood is maintained within a narrow range. For example, the anterior pituitary signals the thyroid to release thyroid hormones. Increasing levels of these hormones in the blood then give feedback to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary to inhibit further signaling to the thyroid gland (Figure 11.24).
Section Summary
Hormones cause cellular changes by binding to receptors on or in target cells. The number of receptors on a target cell can increase or decrease in response to hormone activity.
Hormone levels are primarily controlled through negative feedback, in which rising levels of a hormone inhibit its further release.
The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain. The anterior pituitary receives signals from the hypothalamus and produces six hormones. The posterior pituitary is an extension of the brain and releases hormones (antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin) produced by the hypothalamus. The thyroid gland is located in the neck and is composed of two lobes. The thyroid produces the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin. The parathyroid glands lie on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland and produce parathyroid hormone.
The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys and consist of the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla. The adrenal cortex produces the corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. The adrenal medulla is the inner part of the adrenal gland and produces epinephrine and norepinephrine.
The pancreas lies in the abdomen between the stomach and the small intestine. Clusters of endocrine cells in the pancreas form the islets of Langerhans, which contain alpha cells that release glucagon and beta cells that release insulin. Some organs possess endocrine activity as a secondary function but have another primary function. The heart produces the hormone atrial natriuretic peptide, which functions to reduce blood volume, pressure, and Na+ concentration. The gastrointestinal tract produces various hormones that aid in digestion. The kidneys produce erythropoietin. The thymus produces hormones that aid in the development of the immune system. The gonads produce steroid hormones, including testosterone in males and estrogen and progesterone in females. Adipose tissue produces leptin, which promotes satiety signals in the brain.

