6.1 Sexual Reproduction
Charles Molnar and Jane Gair
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain that variation among offspring is a potential evolutionary advantage resulting from sexual reproduction
- Describe the three different life-cycle strategies among sexual multicellular organisms and their commonalities
- Understand why you could never create a gamete that would be identical to either of the gametes that made yo
However, multicellular organisms that exclusively depend on asexual reproduction are exceedingly rare. Why is sexual reproduction so common? This is one of the important questions in biology and has been the focus of much research from the latter half of the twentieth century until now. A likely explanation is that the variation that sexual reproduction creates among offspring is very important to the survival and reproduction of those offspring. The only source of variation in asexual organisms is mutation. This is the ultimate source of variation in sexual organisms. In addition, those different mutations are continually reshuffled from one generation to the next when different parents combine their unique genomes, and the genes are mixed into different combinations by the process of meiosis. Meiosis is the division of the contents of the nucleus that divides the chromosomes among gametes. Variation is introduced during meiosis, as well as when the gametes combine in fertilization.
The Red Queen Hypothesis
There is no question that sexual reproduction provides evolutionary advantages to organisms that employ this mechanism to produce offspring. The problematic question is why, even in the face of fairly stable conditions, sexual reproduction persists when it is more difficult and produces fewer offspring for individual organisms? Variation is the outcome of sexual reproduction, but why are ongoing variations necessary? Enter the Red Queen hypothesis, first proposed by Leigh Van Valen in 1973.1 The concept was named in reference to the Red Queen’s race in Lewis Carroll’s book, Through the Looking-Glass, in which the Red Queen says one must run at full speed just to stay where one is.
All species coevolve with other organisms. For example, predators coevolve with their prey, and parasites coevolve with their hosts. A remarkable example of coevolution between predators and their prey is the unique coadaptation of night flying bats and their moth prey. Bats find their prey by emitting high-pitched clicks, but moths have evolved simple ears to hear these clicks so they can avoid the bats. The moths have also adapted behaviors, such as flying away from the bat when they first hear it, or dropping suddenly to the ground when the bat is upon them. Bats have evolved “quiet” clicks in an attempt to evade the moth’s hearing. Some moths have evolved the ability to respond to the bats’ clicks with their own clicks as a strategy to confuse the bats echolocation abilities.
Each tiny advantage gained by favorable variation gives a species an edge over close competitors, predators, parasites, or even prey. The only method that will allow a coevolving species to keep its own share of the resources is also to continually improve its ability to survive and produce offspring. As one species gains an advantage, other species must also develop an advantage or they will be outcompeted. No single species progresses too far ahead because genetic variation among progeny of sexual reproduction provides all species with a mechanism to produce adapted individuals. Species whose individuals cannot keep up become extinct. The Red Queen’s catchphrase was, “It takes all the running you can do to stay in the same place.” This is an apt description of coevolution between competing species.
Life Cycles of Sexually Reproducing Organisms
Fertilization and meiosis alternate in sexual life cycles. What happens between these two events depends on the organism. The process of meiosis reduces the resulting gamete’s chromosome number by half. Fertilization, the joining of two haploid gametes, restores the diploid condition. There are three main categories of life cycles in multicellular organisms: diploid-dominant, in which the multicellular diploid stage is the most obvious life stage (and there is no multicellular haploid stage), as with most animals including humans; haploid-dominant, in which the multicellular haploid stage is the most obvious life stage (and there is no multicellular diploid stage), as with all fungi and some algae; and alternation of generations, in which the two stages, haploid and diploid, are apparent to one degree or another depending on the group, as with plants and some algae.
Nearly all animals employ a diploid-dominant life-cycle strategy in which the only haploid cells produced by the organism are the gametes. The gametes are produced from diploid germ cells, a special cell line that only produces gametes. Once the haploid gametes are formed, they lose the ability to divide again. There is no multicellular haploid life stage. Fertilization occurs with the fusion of two gametes, usually from different individuals, restoring the diploid state (Figure 6.2 a).
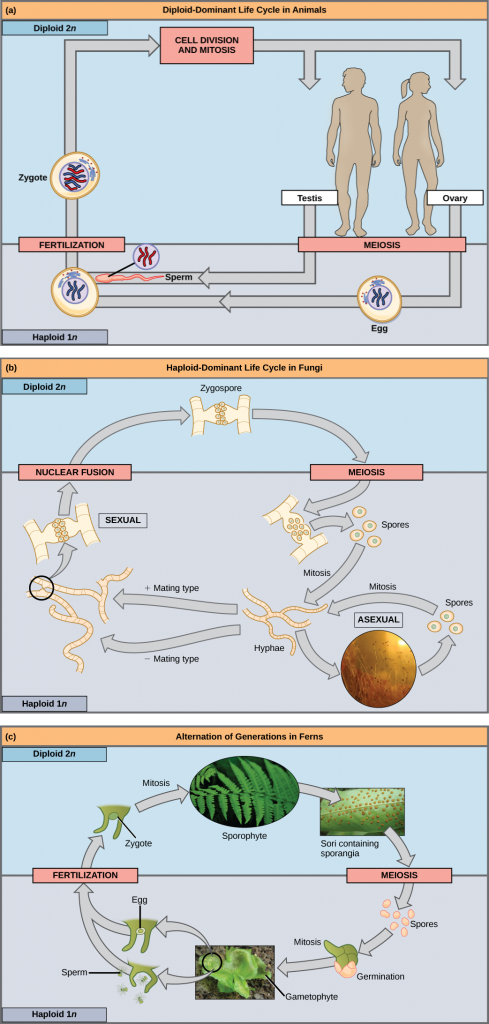
If a mutation occurs so that a fungus is no longer able to produce a minus mating type, will it still be able to reproduce?
Most fungi and algae employ a life-cycle strategy in which the multicellular “body” of the organism is haploid. During sexual reproduction, specialized haploid cells from two individuals join to form a diploid zygote. The zygote immediately undergoes meiosis to form four haploid cells called spores (Figure 6.2 b).
The third life-cycle type, employed by some algae and all plants, is called alternation of generations. These species have both haploid and diploid multicellular organisms as part of their life cycle. The haploid multicellular plants are called gametophytes because they produce gametes. Meiosis is not involved in the production of gametes in this case, as the organism that produces gametes is already haploid. Fertilization between the gametes forms a diploid zygote. The zygote will undergo many rounds of mitosis and give rise to a diploid multicellular plant called a sporophyte. Specialized cells of the sporophyte will undergo meiosis and produce haploid spores. The spores will develop into the gametophytes (Figure 6. 2 c).
Section Summary
Nearly all eukaryotes undergo sexual reproduction. The variation introduced into the reproductive cells by meiosis appears to be one of the advantages of sexual reproduction that has made it so successful. Meiosis and fertilization alternate in sexual life cycles. The process of meiosis produces genetically unique reproductive cells called gametes, which have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Fertilization, the fusion of haploid gametes from two individuals, restores the diploid condition. Thus, sexually reproducing organisms alternate between haploid and diploid stages. However, the ways in which reproductive cells are produced and the timing between meiosis and fertilization vary greatly. There are three main categories of life cycles: diploid-dominant, demonstrated by most animals; haploid-dominant, demonstrated by all fungi and some algae; and alternation of generations, demonstrated by plants and some algae.
Exercises
Glossary
alternation of generations: a life-cycle type in which the diploid and haploid stages alternate
diploid-dominant: a life-cycle type in which the multicellular diploid stage is prevalent
haploid-dominant: a life-cycle type in which the multicellular haploid stage is prevalent
gametophyte: a multicellular haploid life-cycle stage that produces gametes
germ cell: a specialized cell that produces gametes, such as eggs or sperm
life cycle: the sequence of events in the development of an organism and the production of cells that produce offspring
meiosis: a nuclear division process that results in four haploid cells
sporophyte: a multicellular diploid life-cycle stage that produces spores
Footnotes
1 Leigh Van Valen, “A new evolutionary law,” Evolutionary Theory 1 (1973): 1–30.
Chapter 7 in Concepts of Biology: 1st Canadian Edition

