6.3 Sinks and Faucets
Types
There are many types of sinks that meet specific facility needs. Sinks are classified by function and include hand sinks, prep sinks, scullery sinks, mop sinks, pot sinks, bar sinks, and corner sinks. They may be manufactured to National Food Safety regulations. NSF rated sinks are required to be manufactured with radius seams, coved corners and integrally welded drain boards for most effective sanitation. Non- NSF units typically have unground welds and detachable drain boards.
Capacities/Footprints
Local health codes will govern the size of kitchen (scullery) sinks. Some considerations would be the number and size of bowls, water-level depth, backsplash height, and drain board size.
An example of a local regulation could be as follows:
Minimum pot sink bowls should be 20″ X 20″ with at least a 12″ water-level and should have at least three compartments (wash-rinse-sanitize) with two drain boards.
Manufacturing Method
Many sinks are made from stainless steel for durability and easier cleaning.

Common factors
Since the exact code requirements for kitchens are dependent on the local codes and health departments, the requirements vary somewhat from place to place. There are similarities that occur in almost all locations. As a general rule, there are several assumptions that can be made regarding health and plumbing code requirements for kitchen plumbing.
- 140 degrees F hot water is required due to dishwashers requiring 180 degrees F water for final rinse, and a booster heater will be needed to raise the water temperature from 140 degrees F to 180 degrees F.
- At least one hand washing lavatory will be required.
- At least one triple-compartment sink will be required.
- At least one mop basin will be required in or near the kitchen.
- A grease interceptor will be required and should receive waste from all fixtures that carry grease for example pot sinks. Hand washing sinks generally would not be required to drain into a grease trap. Food waste grinders are not allowed to drain into a grease interceptor.
- Floor drains should be provided throughout the space (as required).
- All equipment or sinks that are used to prepare food must be connected indirectly. Sinks used to clean dishes or pots may need to be connected indirectly depending on the Engineers plans and specifications. This may be achieved by emptying indirectly over a floor drain as long as the floor drain is located in a safe area away from kitchen traffic and the drainage will not cause a safety hazard for the kitchen employees.
Commercial Sinks
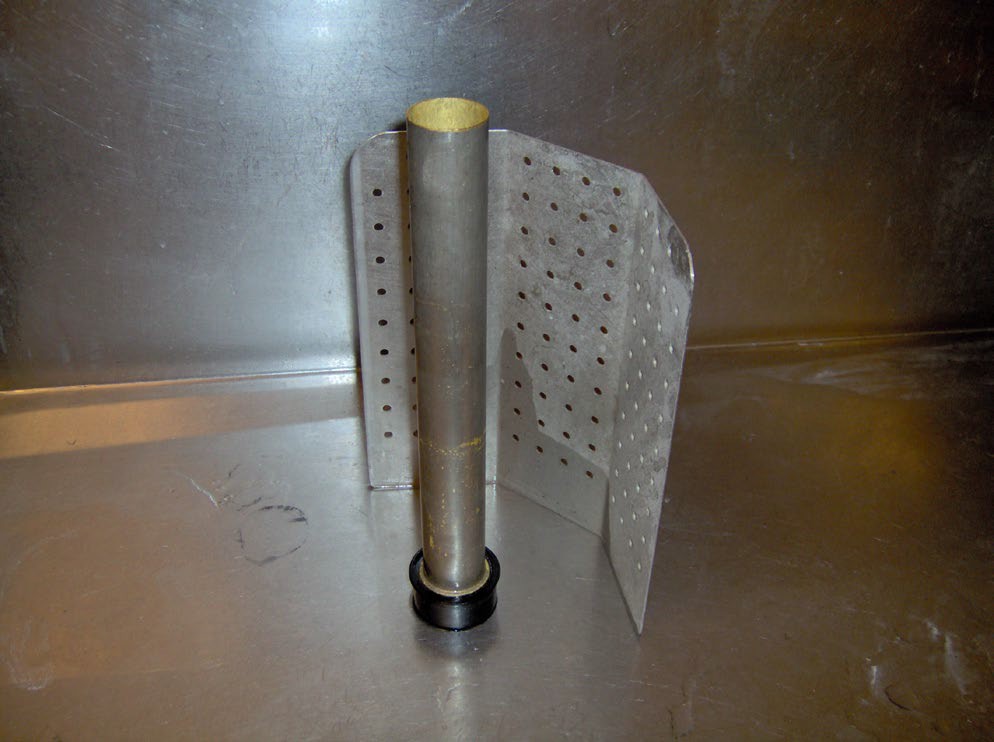
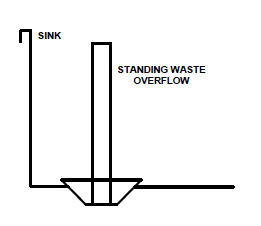
Because of the organic material which drains through a kitchen sink hidden or concealed overflows are not permitted. To prevent sinks from overflowing standpipes are installed into the waste opening which prevents the fixture from draining but allows water to flow over and into the stand pipe. Canada National Plumbing Code 2.2.2.4.1
Some other names for the standpipe are bi-transit waste and standing waste over flow.
Residential sinks use basket strainers with strainers that can be cleaned out after the sink is empty. Commercial sinks outlets do not use this method because of the possibility of the volume of organic materials in the sink water. Most commercial sinks have the drains located in the back corner of the compartments rather than the centre as in residential sinks.
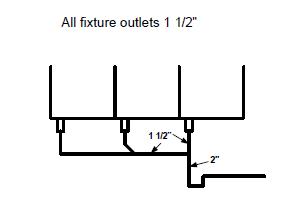
ARTICLE 2.4.9.3. (2 ) of the code states that the fixture outlet pipe that is common to a three-compartment sink shall be one size larger than the largest compartment that it serves.
 |
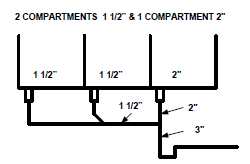 |
Fixture outlet pipe – max. 1.2 meters. The trap must be one size larger than the largest fixture outlet pipe removal.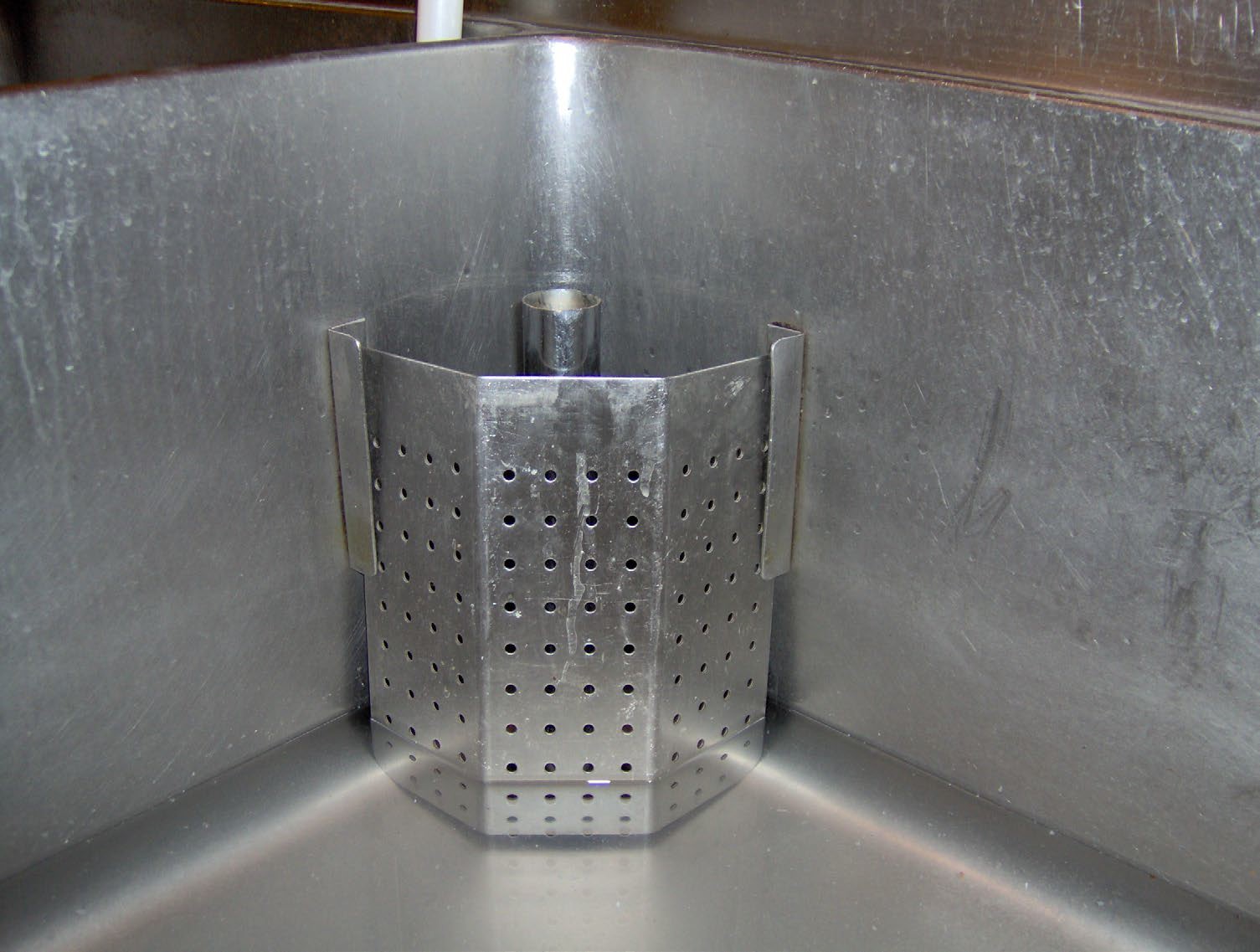
It is important to ensure that the standing waste overflow is about an inch or more lower than the flood level rim of the sink.
 |
 |
Indirect Connections
Fixtures that display, store or are used for food or drink preparation must be connected to the drainage system because of the organic products that these fixtures produce.
Because of the bacteria in drainage systems these types of fixtures must be indirectly connected.[1]
Fixtures that drain clear water waste may be connected to a storm system.[2]
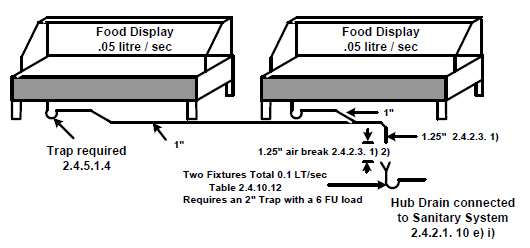
As stated in the Plumbing Code a fixture that is indirectly connected must have an air break of a least 1” or equal to the diameter of the indirect connection whichever is larger. SEC 2.3.3.11. 1) 2)
The drain that the indirect connection drains into is usually a 4” trap sometimes known as a hub drain. The hub drain may be smaller if approved by the authority having jurisdiction. It is very important to ensure that the 4” drain can handle the volume of all the indirect connections that are going to drain into the hub drain. Floor drains may be used for hub drains since the hub drain is usually located in the floor. If the hub drain isn’t installed in the floor than a 4” trap is all that is needed with the indirect connections draining into the outlet. Most fixtures that usually have indirect connections have small flow volumes however splashing could still be a problem.
One option is to increase the area of the opening of the hub drain by installing a funnel drain. The indirect connection openings cannot touch the drain or funnel.

One of the most common errors made when installing indirect connections is that the air break is not high enough or sometimes installed into the hub drain. When this occurs Bacteria may make its way up the indirect connection and into the food display itself causing what food product that comes in contact with the fixture to become contaminated.
- If two fixture outlet pipes from a single fixture that is listed in SEC 2.4.2.1. e) may be directly connected to a branch not less than 1- 1/4 “ and must terminate to form an air break. SEC 2.4.2.3. 1). An Indirect Drain of 1 ¼’ is required to have a minimum of 1 ¼” Air Break.
- The end which forms the air break may drain into a hub drain which is connected to Storm System if the fixture only discharges clear water waste. SEC 2.4.2.1. 1) a) – d)
- Fixture drains from SEC 2.4.2.1 e) i) and ii) must be indirectly connected to the Sanitary System and is extended through the roof when fixtures on 3 or more storeys are connected. SEC 2.4.2.3. 2) ( these fixtures do not discharge clear water waste)
- Fixture drains from SEC 2.4.2.1 e) iii) – vi) must be indirectly connected to the Storm System and is extended through the roof when fixtures on 3 or more storeys are connected. SEC 2.4.2.3. 3) ) ( these fixtures discharge clear water waste)
FOOD DISPLAY UNITS
When indirectly connecting grocery store meat, produce and etc. display cases, extra consideration must be given to the locations of the hub drains. Most units will be shipped with there own Tee, C.O. and trap. These special traps keep the centre line of the trap as high as possible. These types of units are banked together in long isles which make it necessary to install more than one hub drain.
Some of the things that must be considered are:
- Location off outlet on unit ( right or left side )
- Distance between floor and bottom of unit
- Maintaining proper grade of indirect drain
- Size of the outlet and a proper air break must be maintained at hub drain
When determining the size or flow rate of the indirectly connected fixture it is important for the plumber to be able to understand the manufacturer’s literature.
INDIRECT CONNECTIONS TO SANITARY SYSTEM
INDIRECT CONNECTIONS TO STORM SYSTEM
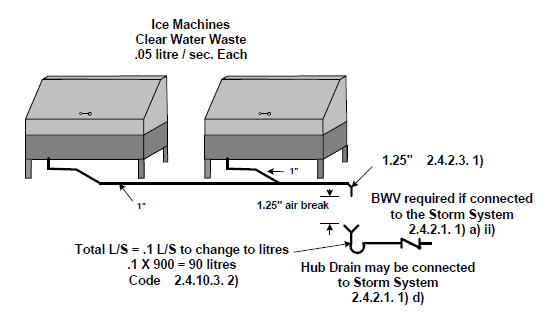
Image Credits
- iFoodEquipment.ca. (n.d.). EFI – three compartment sink. https://ifoodequipment.ca/collections/3-compartment-sinks/products/efi-three- compartment-sink-corner-drains
- Zurn. (n.d.). Open Throat Nickel Bronze Funnel Floor Drain. https://www.zurn.ca/products/building-drainage/floor-drains/finish-floor-shower-drains/zn211bf
