Protein Digestion and Absorption
How do the proteins from foods, denatured or not, get processed into amino acids that cells can use to make new proteins? When you eat food the body’s digestive system breaks down the protein into the individual amino acids, which are absorbed and used by cells to build other proteins and a few other macromolecules, such as DNA. We previously discussed the general process of food digestion, let’s follow the specific path that proteins take down the gastrointestinal tract and into the circulatory system. Eggs are a good dietary source of protein and will be used as our example to describe the path of proteins in the processes of digestion and absorption. One egg, whether raw, hard-boiled, scrambled, or fried, supplies about six grams of protein.
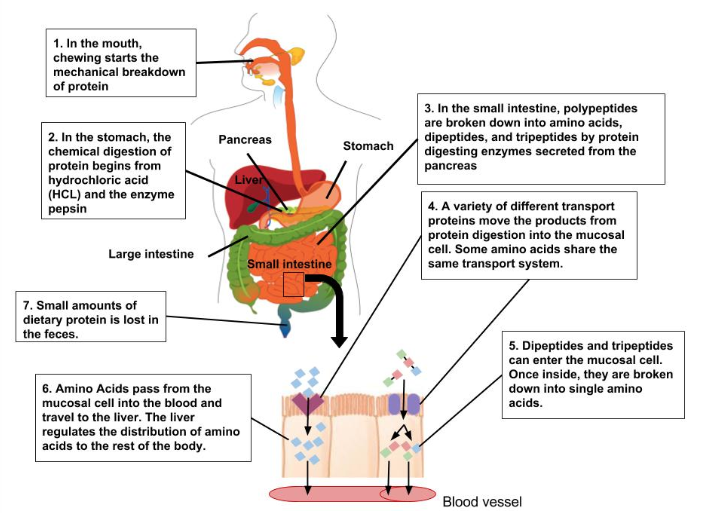
From the Mouth to the Stomach
Unless you are eating it raw, the first step in egg digestion (or any other protein food) involves chewing. The teeth begin the mechanical breakdown of the large egg pieces into smaller pieces that can be swallowed. The salivary glands provide some saliva to aid swallowing and the passage of the partially mashed egg through the esophagus. The mashed egg pieces enter the stomach through the esophageal sphincter. The stomach releases gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid and the enzyme, pepsin, which initiate the breakdown of the protein. The acidity of the stomach facilitates the unfolding of the proteins that still retain part of their three-dimensional structure after cooking and helps break down the protein aggregates formed during cooking. Pepsin, which is secreted by the cells that line the stomach, dismantles the protein chains into smaller and smaller fragments. Egg proteins are large globular molecules and their chemical breakdown requires time and mixing. The powerful mechanical stomach contractions churn the partially digested protein into a more uniform mixture called chyme. Protein digestion in the stomach takes a longer time than carbohydrate digestion, but a shorter time than fat digestion. Eating a high-protein meal increases the amount of time required to sufficiently break down the meal in the stomach. Food remains in the stomach longer, making you feel full longer.
From the Stomach to the Small Intestine
The stomach empties the chyme containing the broken down egg pieces into the small intestine, where the majority of protein digestion occurs. The pancreas secretes digestive juice that contains more enzymes that further break down the protein fragments. The two major pancreatic enzymes that digest proteins are chymotrypsin and trypsin. The cells that line the small intestine release additional enzymes that finally break apart the smaller protein fragments into the individual amino acids. The muscle contractions of the small intestine mix and propel the digested proteins to the absorption sites. In the lower parts of the small intestine, the amino acids are transported from the intestinal lumen through the intestinal cells to the blood. This movement of individual amino acids requires special transport proteins and the cellular energy molecule, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Once the amino acids are in the blood, they are transported to the liver. As with other macronutrients, the liver is the checkpoint for amino acid distribution and any further breakdown of amino acids, which is very minimal. Recall that amino acids contain nitrogen, so further catabolism of amino acids releases nitrogen-containing ammonia. Because ammonia is toxic, the liver transforms it into urea, which is then transported to the kidney and excreted in the urine. Urea is a molecule that contains two nitrogens and is highly soluble in water. This makes it a good choice for transporting excess nitrogen out of the body. Because amino acids are building blocks that the body reserves in order to synthesize other proteins, more than 90 percent of the protein ingested does not get broken down further than the amino acid monomers.
Amino Acids Are Recycled
Just as some plastics can be recycled to make new products, amino acids are recycled to make new proteins. All cells in the body continually break down proteins and build new ones, a process referred to as protein turnover. Every day over 250 grams of protein in your body are dismantled and 250 grams of new protein are built. To form these new proteins, amino acids from food and those from protein destruction are placed into a “pool.” Though it is not a literal pool, when an amino acid is required to build another protein it can be acquired from the additional amino acids that exist within the body. Amino acids are used not only to build proteins, but also to build other biological molecules containing nitrogen, such as DNA, RNA, and to some extent to produce energy. It is critical to maintain amino acid levels within this cellular pool by consuming high-quality proteins in the diet, or the amino acids needed for building new proteins will be obtained by increasing protein destruction from other tissues within the body, especially muscle. This amino acid pool is less than one percent of total body-protein content. Thus, the body does not store protein as it does with carbohydrates (as glycogen in the muscles and liver) and lipids (as triglycerides in adipose tissue).
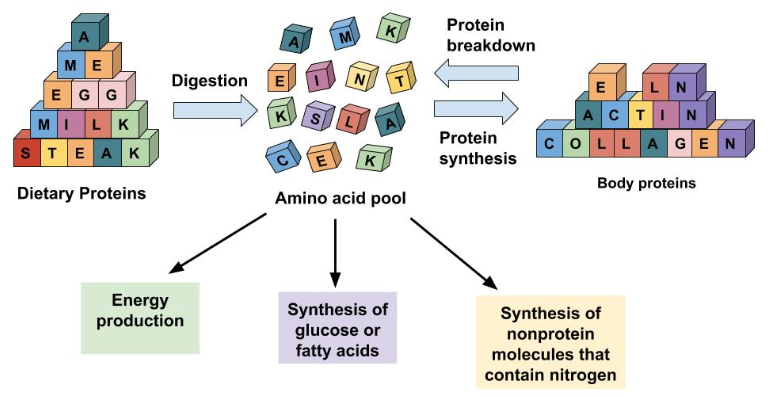
Amino acids in the cellular pool come from dietary protein and from the destruction of cellular proteins. The amino acids in this pool need to be replenished because amino acids are outsourced to make new proteins, energy, and other biological molecules.
Chapter Attribution
Chapter 7.3 in Human Nutrition in a Canadian Context by Karine Hamm published by BCcampus in 2021 under a CC BY License.

