Appendix B. Glossary of Key Symbols and Notation
Lumen Learning
In this glossary, key symbols and notation are briefly defined.
| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| average (indicated by a bar over a symbol—e.g., |
|
| °C | Celsius degree |
| °F | Fahrenheit degree |
| // | parallel |
| ⊥ | perpendicular |
| proportional to | |
| ± | plus or minus |
| 0 | zero as a subscript denotes an initial value |
| α | alpha rays |
| α | angular acceleration |
| α | temperature coefficient(s) of resistivity |
| β | beta rays |
| β | sound level |
| β | volume coefficient of expansion |
| β− | electron emitted in nuclear beta decay |
| β+ | positron decay |
| γ | gamma rays |
| γ | surface tension |
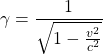 |
a constant used in relativity |
| Δ | change in whatever quantity follows |
| δ | uncertainty in whatever quantity follows |
| ΔE | change in energy between the initial and final orbits of an electron in an atom |
| ΔE | uncertainty in energy |
| Δm | difference in mass between initial and final products |
| ΔN | number of decays that occur |
| Δp | change in momentum |
| Δp | uncertainty in momentum |
| ΔPEg | change in gravitational potential energy |
| Δθ | rotation angle |
| Δs | distance traveled along a circular path |
| Δt | uncertainty in time |
| Δt0 | proper time as measured by an observer at rest relative to the process |
| ΔV | potential difference |
| Δx | uncertainty in position |
| ε0 | permittivity of free space |
| η | viscosity |
| θ | angle between the force vector and the displacement vector |
| θ | angle between two lines |
| θ | contact angle |
| θ | direction of the resultant |
| θb | Brewster’s angle |
| θc | critical angle |
| κ | dielectric constant |
| λ | decay constant of a nuclide |
| λ | wavelength |
| λn | wavelength in a medium |
| μ0 | permeability of free space |
| μk | coefficient of kinetic friction |
| μs | coefficient of static friction |
| ve | electron neutrino |
| π+ | positive pion |
| π− | negative pion |
| π0 | neutral pion |
| ρ | density |
| ρc | critical density, the density needed to just halt universal expansion |
| ρfl | fluid density |
| average density of an object | |
| specific gravity | |
| τ | characteristic time constant for a resistance and inductance (RL) or resistance and capacitance (RC) circuit |
| τ | characteristic time for a resistor and capacitor (RC) circuit |
| τ | torque |
| Υ | upsilon meson |
| Φ | magnetic flux |
| ϕ | phase angle |
| Ω | ohm (unit) |
| ω | angular velocity |
| A | ampere (current unit) |
| A | area |
| A | cross-sectional area |
| A | total number of nucleons |
| a | acceleration |
| aB | Bohr radius |
| ac | centripetal acceleration |
| at | tangential acceleration |
| AC | alternating current |
| AM | amplitude modulation |
| atm | atmosphere |
| B | baryon number |
| B | blue quark color |
| antiblue (yellow) antiquark color | |
| b | quark flavor bottom or beauty |
| B | bulk modulus |
| B | magnetic field strength |
| Bint | electron’s intrinsic magnetic field |
| Borb | orbital magnetic field |
| BE | binding energy of a nucleus—it is the energy required to completely disassemble it into separate protons and neutrons |
| binding energy per nucleon | |
| Bq | becquerel—one decay per second |
| C | capacitance (amount of charge stored per volt) |
| C | coulomb (a fundamental SI unit of charge) |
| Cp | total capacitance in parallel |
| Cs | total capacitance in series |
| CG | center of gravity |
| CM | center of mass |
| c | quark flavor charm |
| c | specific heat |
| c | speed of light |
| Cal | kilocalorie |
| cal | calorie |
| COPhp | heat pump’s coefficient of performance |
| COPref | coefficient of performance for refrigerators and air conditioners |
| cosθ | cosine |
| cotθ | cotangent |
| cscθ | cosecant |
| D | diffusion constant |
| d | displacement |
| d | quark flavor down |
| dB | decibel |
| di | distance of an image from the center of a lens |
| do | distance of an object from the center of a lens |
| DC | direct current |
| E | electric field strength |
| ε | emf (voltage) or Hall electromotive force |
| emf | electromotive force |
| E | energy of a single photon |
| E | nuclear reaction energy |
| E | relativistic total energy |
| E | total energy |
| E0 | ground state energy for hydrogen |
| E0 | rest energy |
| EC | electron capture |
| Ecap | energy stored in a capacitor |
| Eff | efficiency—the useful work output divided by the energy input |
| EffC | Carnot efficiency |
| Ein | energy consumed (food digested in humans) |
| Eind | energy stored in an inductor |
| Eout | energy output |
| e | emissivity of an object |
| e+ | antielectron or positron |
| eV | electron volt |
| F | farad (unit of capacitance, a coulomb per volt) |
| F | focal point of a lens |
| F | force |
| F | magnitude of a force |
| F | restoring force |
| FB | buoyant force |
| Fc | centripetal force |
| Fi | force input |
| Fnet | net force |
| Fo | force output |
| FM | frequency modulation |
| f | focal length |
| f | frequency |
| f0 | resonant frequency of a resistance, inductance, and capacitance (RLC) series circuit |
| f0 | threshold frequency for a particular material (photoelectric effect) |
| f1 | fundamental |
| f2 | first overtone |
| f3 | second overtone |
| fB | beat frequency |
| fk | magnitude of kinetic friction |
| fs | magnitude of static friction |
| G | gravitational constant |
| G | green quark color |
| antigreen (magenta) antiquark color | |
| g | acceleration due to gravity |
| g | gluons (carrier particles for strong nuclear force) |
| h | change in vertical position |
| h | height above some reference point |
| h | maximum height of a projectile |
| h | Planck’s constant |
| hf | photon energy |
| hi | height of the image |
| ho | height of the object |
| I | electric current |
| I | intensity |
| I | intensity of a transmitted wave |
| I | moment of inertia (also called rotational inertia) |
| I0 | intensity of a polarized wave before passing through a filter |
| Iave | average intensity for a continuous sinusoidal electromagnetic wave |
| Irms | average current |
| J | joule |
| Joules/psi meson | |
| K | kelvin |
| k | Boltzmann constant |
| k | force constant of a spring |
| Kα | x rays created when an electron falls into an n = 1 shell vacancy from the n = 3 shell |
| Kβ | x rays created when an electron falls into an n = 2 shell vacancy from the n = 3 shell |
| kcal | kilocalorie |
| KE | translational kinetic energy |
| KE + PE | mechanical energy |
| KEe | kinetic energy of an ejected electron |
| KErel | relativistic kinetic energy |
| KErot | rotational kinetic energy |
| thermal energy | |
| kg | kilogram (a fundamental SI unit of mass) |
| L | angular momentum |
| L | liter |
| L | magnitude of angular momentum |
| L | self-inductance |
| ℓ | angular momentum quantum number |
| Lα | x rays created when an electron falls into an n = 2 shell from the n = 3 shell |
| Le | electron total family number |
| Lμ | muon family total number |
| Lτ | tau family total number |
| Lf | heat of fusion |
| Lf and Lv | latent heat coefficients |
| Lorb | orbital angular momentum |
| Ls | heat of sublimation |
| Lv | heat of vaporization |
| Lz | z-component of the angular momentum |
| M | angular magnification |
| M | mutual inductance |
| m | indicates metastable state |
| m | magnification |
| m | mass |
| m | mass of an object as measured by a person at rest relative to the object |
| m | meter (a fundamental SI unit of length) |
| m | order of interference |
| m | overall magnification (product of the individual magnifications) |
| atomic mass of a nuclide | |
| MA | mechanical advantage |
| me | magnification of the eyepiece |
| me | mass of the electron |
| mℓ | angular momentum projection quantum number |
| mn | mass of a neutron |
| mo | magnification of the objective lens |
| mol | mole |
| mp | mass of a proton |
| ms | spin projection quantum number |
| N | magnitude of the normal force |
| N | newton |
| N | normal force |
| N | number of neutrons |
| n | index of refraction |
| n | number of free charges per unit volume |
| NA | Avogadro’s number |
| Nr | Reynolds number |
| N · m | newton-meter (work-energy unit) |
| N · m | newtons times meters (SI unit of torque) |
| OE | other energy |
| P | power |
| P | power of a lens |
| P | pressure |
| p | momentum |
| p | momentum magnitude |
| p | relativistic momentum |
| ptot | total momentum |
| ptot | total momentum some time later |
| Pabs | absolute pressure |
| Patm | atmospheric pressure |
| Patm | standard atmospheric pressure |
| PE | potential energy |
| PEel | elastic potential energy |
| PEelec | electric potential energy |
| PEs | potential energy of a spring |
| Pg | gauge pressure |
| Pin | power consumption or input |
| Pout | useful power output going into useful work or a desired, form of energy |
| Q | latent heat |
| Q | net heat transferred into a system |
| Q | flow rate—volume per unit time flowing past a point |
| +Q | positive charge |
| −Q | negative charge |
| q | electron charge |
| qp | charge of a proton |
| q | test charge |
| QF | quality factor |
| R | activity, the rate of decay |
| R | radius of curvature of a spherical mirror |
| R | red quark color |
| antired (cyan) quark color | |
| R | resistance |
| R | resultant or total displacement |
| R | Rydberg constant |
| R | universal gas constant |
| r | distance from pivot point to the point where a force is applied |
| r | internal resistance |
| r⊥ | perpendicular lever arm |
| r | radius of a nucleus |
| r | radius of curvature |
| r | resistivity |
| r or rad | radiation dose unit |
| rem | roentgen equivalent man |
| rad | radian |
| RBE | relative biological effectiveness |
| RC | resistor and capacitor circuit |
| rms | root mean square |
| rn | radius of the nth H-atom orbit |
| Rp | total resistance of a parallel connection |
| Rs | total resistance of a series connection |
| Rs | Schwarzschild radius |
| S | entropy |
| S | intrinsic spin (intrinsic angular momentum) |
| S | magnitude of the intrinsic (internal) spin angular momentum |
| S | shear modulus |
| S | strangeness quantum number |
| s | quark flavor strange |
| s | second (fundamental SI unit of time) |
| s | spin quantum number |
| s | total displacement |
| secθ | secant |
| sinθ | sine |
| sz | z-component of spin angular momentum |
| T | period—time to complete one oscillation |
| T | temperature |
| Tc | critical temperature—temperature below which a material becomes a superconductor |
| T | tension |
| T | tesla (magnetic field strength B) |
| t | quark flavor top or truth |
| t | time |
| t1/2 | half-life—the time in which half of the original nuclei decay |
| tanθ | tangent |
| U | internal energy |
| u | quark flavor up |
| u | unified atomic mass unit |
| u | velocity of an object relative to an observer |
| u′ | velocity relative to another observer |
| V | electric potential |
| V | terminal voltage |
| V | volt (unit) |
| V | volume |
| v | relative velocity between two observers |
| v | speed of light in a material |
| v | velocity |
| average fluid velocity | |
| VB − VA | change in potential |
| vd | drift velocity |
| Vp | transformer input voltage |
| Vrms | rms voltage |
| Vs | transformer output voltage |
| vtot | total velocity |
| vw | propagation speed of sound or other wave |
| vw | wave velocity |
| W | work |
| W | net work done by a system |
| W | watt |
| w | weight |
| wfl | weight of the fluid displaced by an object |
| Wc | total work done by all conservative forces |
| Wnc | total work done by all nonconservative forces |
| Wout | useful work output |
| X | amplitude |
| X | symbol for an element |
| notation for a particular nuclide | |
| x | deformation or displacement from equilibrium |
| x | displacement of a spring from its undeformed position |
| x | horizontal axis |
| XC | capacitive reactance |
| XL | inductive reactance |
| xrms | root mean square diffusion distance |
| y | vertical axis |
| Y | elastic modulus or Young’s modulus |
| Z | atomic number (number of protons in a nucleus) |
| Z | impedance |

