26 Muscular System
Learning Objectives
- Identify the anatomy of the muscular system
- Describe the main functions of the muscular system
- Spell the medical terms of the muscular system and use correct abbreviations
- Explore common diseases, disorders, and procedures related to the muscular system
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the muscular system
Muscular System Word Parts
Click on prefixes, combining forms, and suffixes to reveal a list of word parts to memorize for the Muscular System.
Introduction to the Muscular System
When most people think of muscles, they think of the muscles that are visible just under the skin, particularly of the limbs. These are skeletal muscles, so-named because most of them move the skeleton. But there are two additional types of muscles: the smooth muscle and the cardiac muscle. The body has over 600 muscles which contribute significantly to the body’s weight.
Watch this video[1]
Muscular System Medical Terms
Anatomy (Structures) of the Muscular System
Muscle is one of the four primary tissue types of the body, and it is made up of specialized cells called fibers. The body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle (see Figure 17.1). All three muscle tissues have some properties in common; they all exhibit a quality called excitability as their plasma membranes can change their electrical states (from polarized to depolarized) and send an electrical wave called an action potential along the entire length of the membrane. Fascia is fibrous connective tissue that encloses muscles.
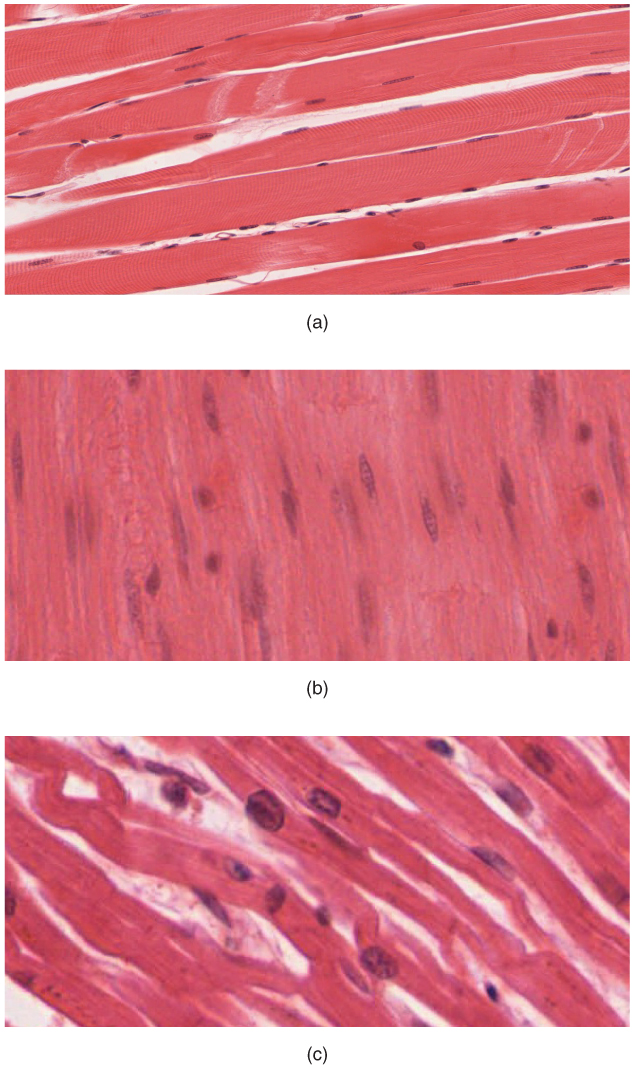
Three Types of Muscle Tissues
- Skeletal – closely associated with the skeletal system. Also known as striated muscles and are responsible for voluntary muscle movement – such as swallowing, etc.
- Smooth – mainly associated with the walls of the internal organs. Also known as visceral muscles and are responsible for involuntary muscle movement – such as breathing, etc.
- Cardiac – heart muscle or myocardium. Its appearance is similar to a skeletal muscle and is responsible for the pumping of blood. It gives the heart beat.
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting gravity to maintain posture. Small, constant adjustments of the skeletal muscles are needed to hold a body upright or balanced in any position. Muscles also prevent excess movement of the bones and joints, maintaining skeletal stability and preventing skeletal structure damage or deformation.
Skeletal muscles are located throughout the body at the openings of internal tracts to control the movement of various substances. These muscles allow functions, such as swallowing, urination, and defecation, to be under voluntary control. Skeletal muscles also protect internal organs (particularly abdominal and pelvic organs) by acting as an external barrier or shield to external trauma and by supporting the weight of the organs.
Skeletal muscles contribute to the maintenance of homeostasis in the body by generating heat. This heat is very noticeable during exercise, when sustained muscle movement causes body temperature to rise, and in cases of extreme cold, when shivering produces random skeletal muscle contractions to generate heat.
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle, so named because the cells do not have striations, is present in the walls of hollow organs like the urinary bladder, uterus, stomach, intestines, and in the walls of passageways, such as the arteries and veins of the circulatory system, and the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. Smooth muscle is also present in the eyes, where it functions to change the size of the iris and alter the shape of the lens; and in the skin where it causes hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear.
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle (see Figure 17.1). Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. An intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave-like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump.
Concept Check
- Compare and contrast the 3 types of muscles tissues.
- Where in the body do you find each of the muscle types?
Physiology (Function) of the Muscular System
The main function of the muscular system is to assist with movement. Muscles work as antagonistic pairs. As one muscle contracts, the other muscle relaxes. This contraction pulls on
the bones and assists with movement. Contraction is the shortening of the muscle fibers while relaxation lengthens the fibers. This sequence of relaxation and contraction is influenced by the nervous system.
Muscles also work to keep the posture of the body. This is done through muscle contraction where the trunk is kept straight either when sitting or standing.
Naming of Muscles
There are many nomenclatures for naming muscles. Some of these include:
- divisions – biceps, triceps, quadriceps
- size – maximus (largest), minimus (smallest)
- shape – deltoid (triangular), trapezious (trapezoid)
- action – flexor (to flex), adductor (towards midline of body)
| EXAMPLE | WORD | LATIN ROOT 1 | LATIN ROOT 2 | MEANING | TRANSLATION |
| abductor digiti minimi | abductor | ab = away from | duct = to move | a muscle that moves away from | A muscle that moves the little finger or toe away |
| digiti | digitus = digit | n/a | refers to a finger or toe | ||
| minimi | minimus = mini, tiny | n/a | little | ||
| adductor digiti minimi | adductor | ad = to, toward | duct = to move | a muscle that moves towards | A muscle that moves the little finger or toe toward |
| digiti | digitus = digit | n/a | refers to a finger or toe | ||
| minimi | minimus = mini, tiny | n/a | little |
Muscular System Medical Abbreviations
Common Diseases and Disorders/h2>
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is caused by the inability of the body to make dystrophin (a muscle protein). This causes the muscles to become weak as the person ages. This disease primarily effects boys and signs and symptoms typically present before the age of five. Signs and symptoms may include frequent falls and trouble keeping up with peers. Since all muscles are affected, the person will eventually require a wheelchair and assistance with breathing (Muscular Dystrophy Canada, 2020). To learn more please visit Muscular Dystrophy Canada’s neuromuscular disorders web page.
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is caused by an interruption to the normal development of a person’s brain leading to weakness with muscles. Depending on the area of the brain that is affected, signs and symptoms will vary in the type and severity between individuals. Balance and coordination are often challenging due the inability to control muscles (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019; Ontario Federation for Cerebral Palsy, 2018). To learn more about Cerebral palsy please visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome may present with pain, numbness or weakness to the hand(s) caused by pressure on the median nerve. Some causes for this pressure are work related such as keyboarding with improper body mechanics, illness such as arthritis, and even pregnancy (Healthwise Staff, 2018). To learn more, visit Health Link BC’s Carpal Tunnel web page.
Paralysis
- Paresis – a partial paralysis wherein there is still some control of the muscles
- Paraplegia – paralysis that affects both legs and lower part of the body.
- Quadriplegia – affects both arms, both legs and sometimes from the neck down
- Hemiplegia – affects one side of the body. For example, the arm and leg on the same side of the body (Cleveland Clinic, 2017)
To learn more about paralysis, please visit the Cleveland Clinic’s Paralysis information web page.
Sprain and Strain
A sprain is an injury to a joint whereby a ligament is stretched or torn.
A strain is an injury to a muscle whereby a tendon is stretched or torn.
Diagnostic Procedures
Electromyography (EMG) is a procedure that assesses the function of nerve cells that control muscles. Electrodes, either attached to the skin or inserted into the muscle, allow for the recording of electrical impulses. EMG can indicate functional problems with the peripheral nerves, muscles, or with the signals between the nerves and the muscles. This is just one test in a series of tests that assist in the diagnosis of neuromuscular disorders (Mayo Clinic Staff, 2019; Body Restoration, 2020). To learn more, please visit the Mayo Clinic’s Electromyography web page.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a test that uses radio frequency waves and a magnetic field to produce clear images that aid in the diagnosis of a wide range of conditions (London Health Sciences Centre, 2020). Leung (2017) notes that there has been increased clinical use in using MRI for the treatment and monitoring of muscular disorders due to the high-quality MRI images that distinguish skeletal muscles from fat (para. 4).
Range of Motion Testing is a diagnostic procedures used to determine the amount of movement around a specific joint.
Medical Specialties Related to Muscular System
Orthopedic Surgeon
Orthopedic Surgeons are medical doctors who complete an additional 5-years of specialized training in the prevention, diagnosis, treatment and surgery of disorders and diseases related to the musculoskeletal systems (Canadian Medical Association, 2018). For more details please visit the Canadian Medical Association’s page on Orthopedic Surgery (PDF file).
Neurologist
Neurologists are medical doctors who complete an additional 5 years of specialized training in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders and conditions related to the brain, spinal cord, nerves and muscles (Canadian Medical Association, 2018a). For more details visit the Canadian Medical Association’s page on Neurology profile (PDF File).
Kinesiologist
Kinesiologists are regulated health-care professionals with a four-year degree in kinesiology or related discipline. In Ontario, a kinesiologist must be registered and in good standing with the College of Kinesiologists of Ontario. Kinesiologists work in a variety of settings that assist people with pain management, injury prevention, and health promotion through biomechanics (College of Kinesiologists of Ontario, n.d.). To learn more, visit the College of Kinesiologists of Ontario’s website.
Muscular System Vocabulary
Antagonistic
In opposition to each other.
Cardiac muscle
The heart muscle also known as the myocardium. Its appearance is similar to skeletal muscle. It pumps blood and gives the heart beat.
Electromyography (EMG)
Measures muscle response or electrical activity in response to a nerve’s stimulation of the muscle.
Fibromyalgia
Pain in the fibrous tissues of muscles.
Hemostasis
Biological process that results in stable equilibrium.
Hemiplegia
Paralysis that effects one side of the body.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Radio frequency waves and a strong magnetic field provide clear and detailed pictures of internal organs and tissues.
Myasthenia Gravis
Grave or serious muscle weakness.
Paraplegia
Paralysis that affects both legs and lower part of the body.
Paresis
Partial paralysis wherein there is still some control of the muscles.
Quadriplegia
Affects both arms, both legs and sometimes from the neck down.
Skeletal muscle
Also known as striated muscles. Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary muscle movement.
Smooth muscle
Also known as visceral muscles. Smooth muscle is mainly associated with the walls of internal organs. Smooth muscles are responsible for involuntary muscle movement.
Sprain
Injury to a joint whereby a ligament is stretched or torn.
Strain
Injury to a muscle whereby a tendon is stretched or torn.
Test Yourself
References
Body Restoration. (2020). Electromyography (EMG) test: Diagnosing nerve and muscle injuries. https://bodyrestoration.ca/electromyography-test-edmonton-2/
Canadian Medical Associatoin. (2018, August). Orthopedic surgery profile. CMA Specialty Profiles. https://www.cma.ca/sites/default/files/2019-01/orthopedic-surgery-e.pdf
Canadian Medical Association. (2018a, August). Neurology profile. CMA Specialty Profiles. https://www.cma.ca/sites/default/files/2019-01/neurology-e.pdf
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019, April 30). What is cerebral palsy? CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/cp/facts.html
College of Kinesiologists of Ontario. (n.d.). About kinesiology. https://www.coko.ca/patients-and-clients/about-kinesiology/
[CrashCourse]. (2015, July 15). Muscles, part 2 – organismal level: Crash course A&P #22 [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/I80Xx7pA9hQ
Healthwise Staff. (2018, September 20). Carpal tunnel syndrome: Topic overview. HealthLink BC. https://www.healthlinkbc.ca/health-topics/hw213308
Leung, J. (2016, November 25). Magnetic resonance imaging patterns of muscle involvement in genetic muscle diseases: a systematic review. Journal of Neurology, 264(7), 1320-1333. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fs00415-016-8350-6
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2019, May 21). Electromyography (EMG). Mayo Clinic Patient Care and Information. https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/emg/about/pac-20393913
Muscular Dystrophy Canada. (2020). About Neuromuscular disorders: Duchenne muscular dystrophpy. https://muscle.ca/discover-md/types-of-neuromuscular-disorders/
Ontario Federation for Cerebral Palsy. (2018). About cerebral palsy. OFCP. https://www.ofcp.ca/about-cerebral-palsy
Image Descriptions
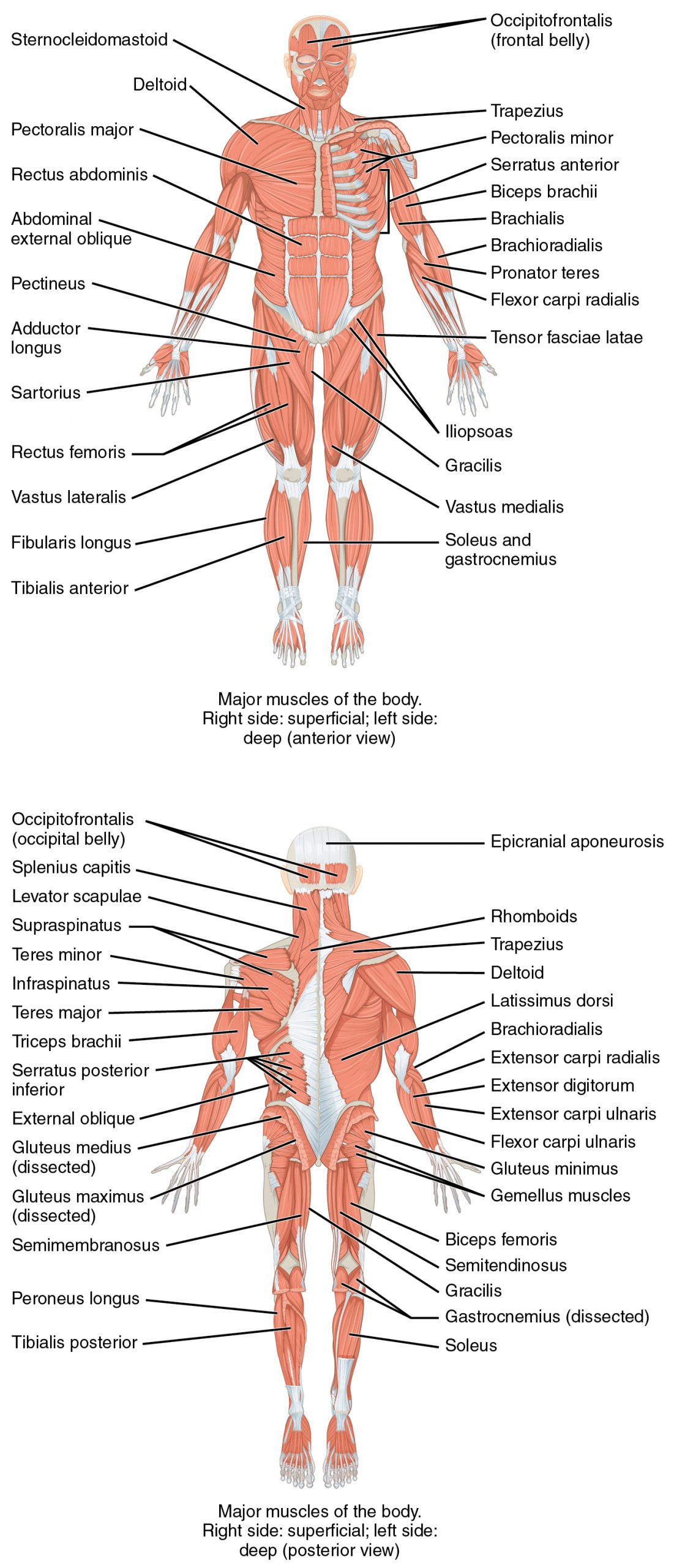
Figure 17.2 image description: The top panel shows the anterior view of the human body with the major muscles labeled. Labels read (from top, head): occipitofrontalis (frontal belly), sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, deltoid, pectorailis minor, serratus anterior, pectoralis major, arm muscles: biceps brachii, brachialis, brachioradialis, pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, abdomnial: rectus abdominis, abdominal external oblique, lower body: tensor fasciae latae, illiopsoas, penctineus, adductor longus, sartorius, gracilis, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vasus medialis, biularis longus, tibialis anterior. The bottom panel shows the posterior view of the human body with the major muscles labeled. Labels read (from top, head, left side): epicranial aponeurosis, occipitofrontalis, splenius capitis, levator scapulae, rhombus, trapezius, supraspinatus, teras minor, infraspinatus, teres major, triceps brachii, seratus posterior inferior, external oblique, lower body: gluteus medius, gluteus maximus, semimebranosus, peroneus longus, tibialis posterior, (right side, from top) trapezius, deltpid, latissimus dorsi, arm: brachioradialis, extersor carpi radialis, extensor digitorum, extensor carpi ulnaris, flexor carpi ulnaris, lower body: gluteus minimus, gemellus muscles, biceps femoris, semitendinosus, gracilis, gastrocnemius, soleus. [Return to Figure 17.2].
Unless otherwise indicated, this chapter contains material adapted from Anatomy and Physiology (on OpenStax), by Betts, et al. and is used under a a CC BY 4.0 international license. Download and access this book for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction.
- Media 17.1 Muscles, Part 2 - Organismal Level: Crash Course A&P #22 [Online video]. Copyright 2015 by CrashCourse. ↵
Also known as striated muscles. Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary muscle movement.
Is the heart muscle also known as the myocardium. Its appearance is similar to skeletal muscle. It pumps blood and gives the heart beat.
Also known as visceral muscles. Smooth muscle is mainly associated with the walls of internal organs. Smooth muscles are responsible for involuntary muscle movement.
biological process that results in stable equilibrium
in opposition to each other
naming conventions

