8 The Chemistry of Water
Learning Objectives
At the end of this unit, you should be able to:
I. Explain the biological importance of water.
II. Specify the percentage of body weight that is composed of water and estimate the amount of body water you contain in litres.
III. Describe the distribution of body water.
Learning Objectives and Guiding Questions
At the end of this unit, you should be able to complete all the following tasks, including answering the guiding questions associated with each task.
I. Explain the biological importance of water.
- For each of the four biologically important properties of water:
- Identify the property.
- Describe its importance in the human body.
II. Specify the percentage of body weight that is composed of water and estimate the amount of body water you contain in litres.
- Given your (approximate) body weight, calculate the amount of water you contain, in litres. You may use a calculator if necessary, but must clearly show all your work!
III. Describe the distribution of body water.
- For each of the major fluid compartments of the human body:
- Name the compartment.
- Define the compartment by specifying its location in the human body.
- Specify the percentage of body fluid volume made up by that compartment.
As much as 70 percent of a human’s body weight is water. This water is contained both within the cells and between the cells that make up tissues and organs. Its several roles make water indispensable to human functioning.
Biological Importance of Water
Water as a Lubricant and Cushion
Water is a major component of many of the body’s lubricating fluids. Just as oil lubricates the hinge on a door, water in synovial fluid lubricates the actions of body joints, and water in pleural fluid helps the lungs expand and recoil with breathing. Watery fluids help keep food flowing through the digestive tract, and ensure that the movement of adjacent abdominal organs is friction free.
Water also protects cells and organs from physical trauma, cushioning the brain within the skull, for example, and protecting the delicate nerve tissue of the eyes. Water cushions a developing fetus in the mother’s womb as well.
Water as a Heat Sink
A heat sink is a substance or object that absorbs and dissipates heat but does not experience a corresponding increase in temperature. In the body, water absorbs the heat generated by chemical reactions without greatly increasing in temperature. Moreover, when environmental temperature soars, the water stored in the body helps keep the body cool. This cooling effect happens as warm blood from the body’s core flows to the blood vessels just under the skin and is transferred out to the environment as radiant heat. At the same time, sweat glands release warm water in sweat. For evaporation of this water to occur, the hydrogen bonds between the water molecules must be broken, requiring a relatively high amount of energy that in part includes heat. This removal of heat by evaporation results in a cooling of the blood in the body’s periphery, near the surface of the skin, which then circulates back to the body core and cools the body.
Water as a Component of Liquid Mixtures
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances, each of which maintains its own chemical identity. In other words, the constituent substances are not chemically bonded into a new, larger chemical compound. The concept is easy to imagine if you think of powdery substances such as flour and sugar; when you stir them together in a bowl, they obviously do not bond to form a new compound. The room air you breathe is a gaseous mixture, containing argon, molecules of nitrogen and oxygen, and one compound— carbon dioxide.
For cells in the body to survive, they must be kept moist in a water-based liquid called a solution. In chemistry, a liquid solution consists of a solvent that dissolves a substance called a solute. An important characteristic of solutions is that they are homogeneous; that is, the solute molecules are distributed evenly throughout the solution. If you were to stir a teaspoon of sugar into a glass of water, the sugar would dissolve into sugar molecules separated by water molecules. The ratio of sugar to water in the left side of the glass would be the same as the ratio of sugar to water in the right side of the glass. If you were to add more sugar, the ratio of sugar to water would change, but the distribution—provided you had stirred well—would still be even.
The Role of Water in Chemical Reactions
Two types of chemical reactions involve the creation or the consumption of water: dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis.
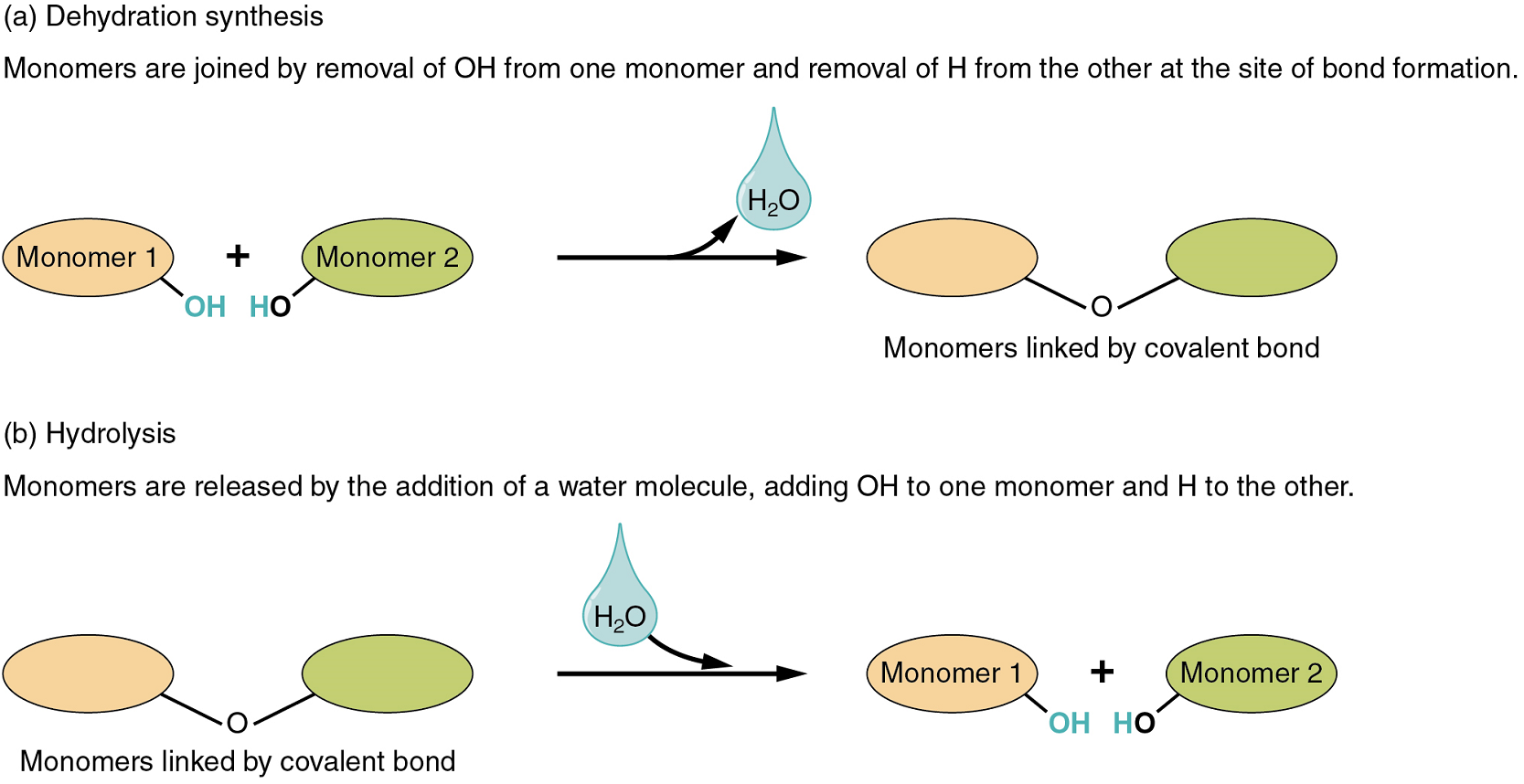
- In dehydration synthesis, one reactant gives up an atom of hydrogen and another reactant gives up a hydroxyl group (OH) in the synthesis of a new product. In the formation of their covalent bond, a molecule of water is released as a byproduct (Figure 1). This is also sometimes referred to as a condensation reaction.
- In hydrolysis, a molecule of water disrupts a compound, breaking its bonds. The water is itself split into H and OH. One portion of the severed compound then bonds with the hydrogen atom, and the other portion bonds with the hydroxyl group.
These reactions are reversible, and play an important role in the chemistry of organic compounds (which will be discussed shortly).
Fluid Compartments in the Human Body
Body Water Content
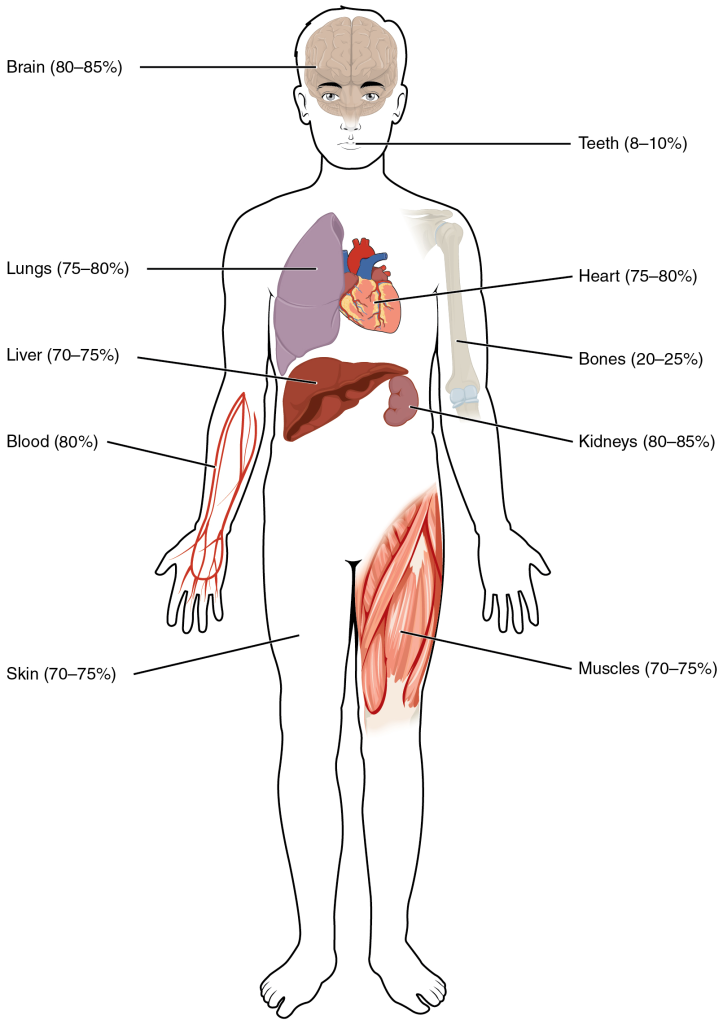
Human beings are mostly water, ranging from about 75 percent of body mass in infants to as low as 45 percent in old age. In adults, the average percent of body mass in women is 50 percent, whereas in men the average is 60 percent. The percent of body water changes with development, because the proportions of the body given over to each organ and to muscles, fat, bone, and other tissues change from infancy to adulthood (Figure 2).
Fluid Compartments
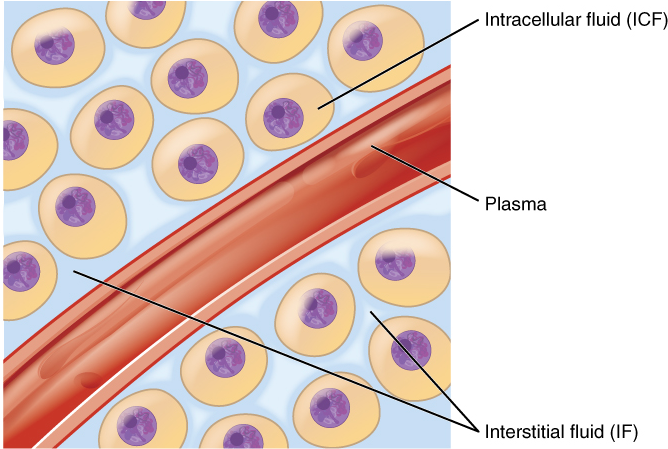
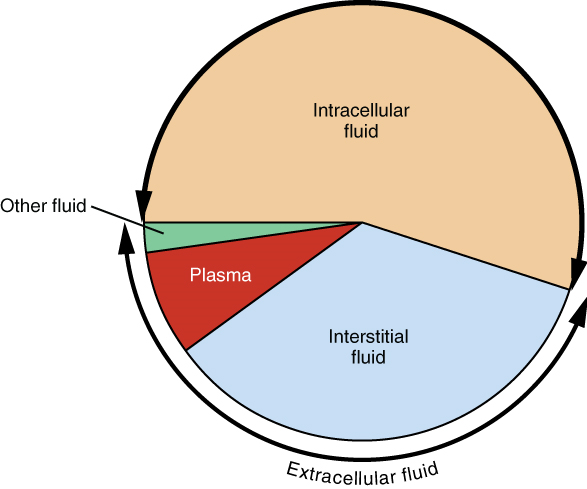
Body fluids can be discussed in terms of their specific fluid compartment, a location that is largely separate from another compartment by some form of a physical barrier. The intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment is the system that includes all fluid enclosed in cells by their plasma membranes. Extracellular fluid (ECF) surrounds all cells in the body. Extracellular fluid has two primary constituents: the fluid component of the blood (called plasma) and the interstitial fluid (IF) that surrounds all cells not in the blood (Figure 3).
1. Intracellular Fluid: The intracellular fluid lies within cells and is the principal component of the cytosol/cytoplasm. The intracellular fluid makes up approximately two thirds (about 60 percent) of the total water in the human body, and in an average-size adult male, the intracellular fluid accounts for about 25 litres (seven gallons) of fluid (Figure 4). This fluid volume tends to be very stable, because the amount of water in living cells is closely regulated. If the amount of water inside a cell falls to a value that is too low, the cytosol becomes too concentrated with solutes to carry on normal cellular activities; if too much water enters a cell, the cell may burst and be destroyed.
2. Extracellular Fluid: The extracellular fluid accounts for the other one-third of the body’s water content. Approximately 20 percent of the extracellular fluid is found in plasma. Plasma travels through the body in blood vessels and transports a range of materials, including blood cells, proteins (including clotting factors and antibodies), electrolytes, nutrients, gases, and wastes. Gases, nutrients, and waste materials travel between capillaries and cells through the interstitial fluid. Cells are separated from the interstitial fluid by a selectively permeable cell membrane that helps regulate the passage of materials between the interstitial fluid and the interior of the cell.
The body has other water-based extracellular fluid. These include the cerebrospinal fluid that bathes the brain and spinal cord, lymph, the synovial fluid in joints, the pleural fluid in the pleural cavities, the pericardial fluid in the cardiac sac, the peritoneal fluid in the peritoneal cavity, and the aqueous humor of the eye. Because these fluids are outside cells, these fluids are also considered components of the extracellular fluid compartment.
Watch this Amoeba Sisters’ video to learn more about the properties of water!
Watch this CrashCourse video to learn more about the importance of water and its chemical properties.
Practice Questions
Biological importance of water
Fluid compartments in the human body
Attribution Note: Chapter remixed from Douglas College Human Anatomy & Physiology I by the Douglas College Biology Department.
Thick, lubricating fluid that fills the interior of a synovial joint.
Substance that acts as a lubricant for the visceral and parietal layers of the pleura during the movement of breathing.
Scatter or break up.
Dipole-dipole bond in which a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom is weakly attracted to a second electronegative atom.
A substance composed of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds.
In chemistry, a homogeneous liquid mixture in which a solute is dissolved into molecules within a solvent.
Component of a solution, the substance that dissolves the solute.
Component of a solution, the substance dissolved in a solvent.
Condition in which solute molecules are distributed equally in a solution.
Chemical reaction in which reactants combine to form a new compound, with one reactant gives up an atom of hydrogen and another reactant gives up a hydroxyl group (OH).
A functional group, OH, present in many organic compounds including alcohols.
Chemical reaction in which a molecule water is split into H and OPH, thereby breaking a bond and severing a compound.
Fluid inside cells.
Fluid outside cells (plasma or interstitial fluid).
An extracellular fluid, the fluid component of blood.
Extracellular fluid in the small spaces between cells not contained within blood vessels.
Clear, semi-fluid medium of the cytoplasm, made up mostly of water.
Internal material between the cell membrane and nucleus of a cell, mainly consisting of a water-based fluid called cytosol, within which are all the other organelles and cellular solute and suspended materials.
(Also, coagulation factors) group of 12 identified substances active in coagulation.
(Also, immunoglobulin) antigen-specific protein secreted by plasma cells.
A solution containing ions; sometimes referring to ions themselves.
Smallest of the blood vessels where physical exchange occurs between the blood and tissue cells surrounded by interstitial fluid.
Feature of any barrier that allows certain substances to cross but excludes others.
Circulatory medium within the CNS that is produced by ependymal cells in the choroid plexus filtering the blood.
Fluid contained within the lymphatic system, consisting of interstitial fluid, leukocytes (white blood cells), proteins (including antibodies) and fats.
The space between the visceral and parietal pleurae.
Fluid found in the pericardium.
Cavity surrounding the heart filled with a lubricating serous fluid that reduces friction as the heart contracts (also, pericardial cavity or cardiac sac).

