7.1 Researching Your Prospect: Going Deeper
Spring break is just around the corner. You and your friends definitely want to go away somewhere great. You decide on Cancún, Mexico, as a destination. Since you want to get the best plane fare and hotel rate, you will have to book early. That means planning, coordinating, and even doing some research on the area. You want everything to be perfect—after all, this is spring break. Just as preparation made your spring break trip come together perfectly, preparation also makes a sales call successful. By now you have identified and qualified your prospects, you have come up with an action plan, and you are probably eager to get down to business. However, you cannot just call your prospect or show up at their door without doing your homework first.
How big is their business? What are their business goals? What is the company culture? Are they already doing business with any of your competitors? In what ways do your products or services present a solution they could use?[1] Customer-focused relationship selling demands that you place top priority on uncovering customer needs. Doing your research and coming prepared gets your prospect’s attention and shows them that you care. It gives you the power to sell adaptively and puts you ahead of your competitors. Keep in mind that when someone ultimately decides to do business with you, they are trusting you with one of the things that is most important to them—their money.
Gather Information
By the time you’re ready for the pre-approach, you’ve already done some initial research as part of the qualifying process. With the pre-approach, you take your research to the next level; you find out as much as you possibly can about the company or individual with whom you want to do business. As marketing and strategy expert Noel Capon says, a thorough understanding of your prospect’s business processes and challenges gives you the crucial insights you’ll need to offer specific, workable solutions your customers can use. Gathering this information demonstrates personal commitment and boosts your credibility with your prospects.[2]
It’s particularly important to identify your key accounts, your current customers who are—or have the potential to be—your most significant sources of sales. Maybe you sell insurance, and you’ve contracted with a large restaurant chain to provide their employee health and dental plan. This key account is one of the largest companies with whom you do business, so you make an extra effort to stay informed about developments that affect this company. You’ve recently received a news alert that due to an unstable economy the restaurant chain has decided to cut employee hours. As a result, many of the staff members are now working part-time and no longer qualify for full health benefits. Based on this information, you call your contact at the company and offer to provide a more flexible and less expensive partial employee benefits package for which their part-time workers could still qualify. You tell them that this solution will serve their company’s need to cut costs and will allow them to retain employees who might otherwise become dissatisfied and leave. Whether you are contacting new or existing customers, it is important to have your specific call objectives in mind and to clearly map out the information you have already gathered about the company so that you can refer to it during the sales call. You can keep this information organized using a precall planning worksheet that lists the key company statistics you’ve identified as part of your research and includes a checklist detailing the purpose of the call: the information you’d like to learn about the company, the solutions or key facts you plan to communicate, and any other goals you hope to achieve. The worksheet does not have to be complex; it can be as straightforward as the sample in Figure 8.1 “Precall Planning Worksheet”.
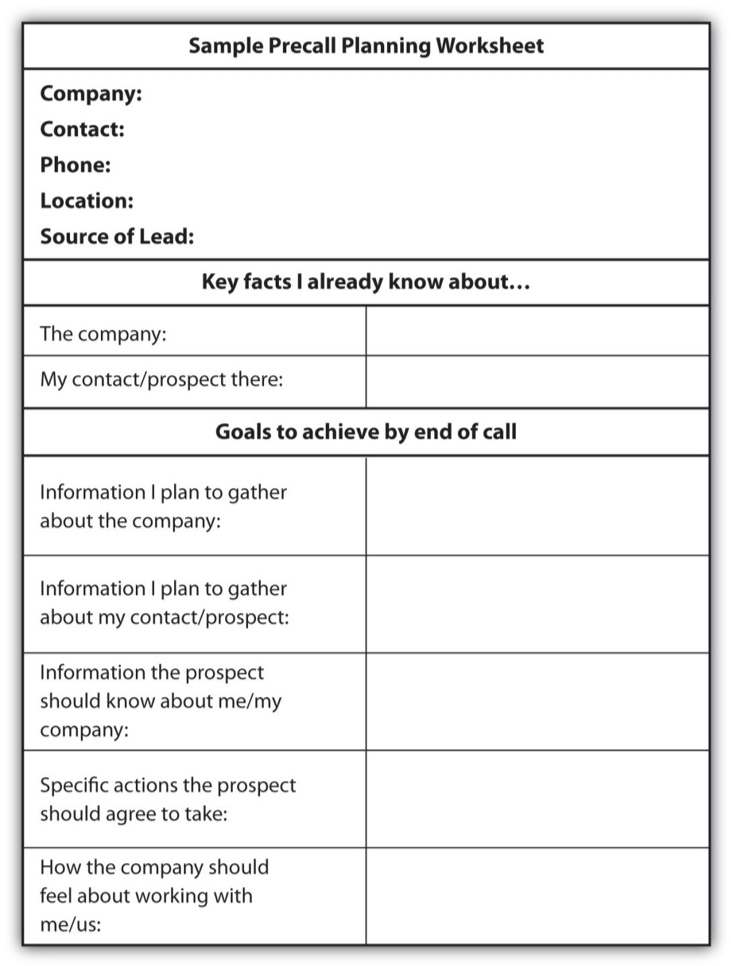
Listing your goals in writing before you make a sales call gives you the power to measure the success of your call. Did you get the information you needed? Did you communicate the information you listed in your checklist? If not, how can you adapt your approach and set goals for your next sales call?
Going Deeper with the Fundamentals: What You’ll Want to Know
The first sales call (or calls) is often an extension of the qualifying process (Remember MANA from Chapter 7). Even if the company passes initial qualification, as you learn more you might find out that they are not your ideal customers after all. You might discover that your contact at the company is about to leave or change positions. Or you might realize that the company’s current situation isn’t one in which they’re willing or able to buy. The following are some things you will want to know as you research the company during your pre-approach.
1. About the Company
- Demographics. Understanding the basics will help you ensure the company fits your ideal prospect profile and allow you to tailor your solution to fit the company’s particular situation. What kind of business is it? How large is the business? How many locations do they have? How many people work for them? Where is the home office located? How many years have they been in business?
- Company news. Tracking company news is another way to discover opportunities for sales. Has the company put out any recent press releases? (You can generally find these on the company Web site in the investor relations, press release, or press room section.) Has the company recently appeared in the news? Setting up Google News Alerts for your current and potential customers will keep you up-to-date on this.
Don’t just read the news; creatively think about what the news is telling you about selling opportunities with a prospect. For example, if you were selling paper goods (cups, lids, straws, bags, cup jackets, napkins, etc.) to coffee shops, you would have read a press release about the test marketing of McCafés several months before the national launch. Then you would have read about the announcement of the national launch a few months before it was planned to occur. These press releases are selling opportunities. You might think it would only be a selling opportunity if you were selling to McDonald’s, but that’s not true. The fact is McDonald’s announced that it was about to expand the market for premium coffee. That’s an opportunity to help your customers and prospects. For example, what if you suggested that your customers and prospects print an advertisement on their bags, napkins, cups, and cup jackets to announce a promotion called “Morning Joe Wake-up Call”? “Buy a cup of coffee every day for ten days and get a free cup of Joe!” This helps increase their sales, which ultimately increases your sales. You could bring this idea to your customer or prospect in advance of the McCafé launch and discuss how your idea can help him build his brand prior to the competitive effort. Now that’s using company news to drive sales.[3]
- Financial performance. Keeping up-to-date on the company’s financial performance will help you determine whether your prospect is currently able to buy, which might lead you to discover sales opportunities. All publicly held companies are required to post their quarterly earnings on their websites. Generally, there will be a link for “investors” or “investor relations” on the company home page that will take you to financial data, including a recording of the company’s quarterly earnings conference call. It’s a good idea to listen to these conference calls to learn important information about the company’s strategy and financial performance.
2. About the Company’s Customers
- Customer demographics. Are the company’s products used by businesses or individual consumers? If consumers, what age, education, and income level? If businesses, what size and kind of businesses? Knowing the organization’s customer demographics will help you tailor your solution to the company. For instance, if you’re selling clothing designs to Old Navy, knowing that the company appeals to families and that it draws in value-conscious customers, you might send them samples from your more basic and reasonably priced clothing line, rather than your top-of-the-line products or your trendiest designs.
- Size of customer base. In B2B sales, it’s important to know whether your prospect serves many customers or primarily works with a few large accounts. Microsoft, for example, sells its products to large corporations, but they also deal with individual consumers. Some companies, on the other hand, work with a few large accounts, so their success is very dependent on the success of their key customers. If your prospect is a sporting goods manufacturer that only sells its products to Bass Pro Shop, their financial performance will affect the performance of your prospect’s business.
- What customers are saying about your prospect. You can learn a lot about a company by paying attention to its reputation with customers. If the business has a lousy customer service record, they might not treat their vendors well either. This is why it is worthwhile to read customer reviews as part of your qualifying process. For instance, if you do business in the tourism industry, you might look through Trip Advisor or Yelp for reviews about your prospect. Amazon has reviews for all of their vendors and for large companies, doing a Google search will often bring up customer reviews on the organization, or you can try a Web site like Epinions. For local companies, try searching your regional Better Business Bureau (BBB) to see if any customer complaints have been filed against the company.
3. About the Current Buying Situation
- Type of purchase. In the chapter “Why and How People Buy” you learned the different types of buys—straight rebuy, modified rebuy, or strategic alliance. Knowing that information is extremely valuable during your pre-approach research. Is the customer making a first-time purchase of the product? (For instance, maybe you’re selling disaster recovery services to a company that has previously lived with the risk of not having their data backed up.) Or will this purchase be a rebuy? Maybe the customer is an interior design firm. The firm already buys paint from a certain supplier but is thinking of making a modified rebuy: purchasing a more environmentally friendly line of paints, either from the same supplier or from someone else (hopefully you!). On the other hand, maybe the design firm is already buying from you and is perfectly happy with the paints and with you as a supplier, so it decides to make a straight rebuy of the same product. It’s also possible that your prospect is considering a strategic alliance with your company in which your organizations would make an agreement to share resources. For example, Chapters bookstores only uses Starbucks in their stores[4] and Petro Canada only has A & W in their gas stations. Knowing the type of purchase will help you position your solution to best fit the situation.
- Competitor/current provider. If your prospect is already buying from another company, you’ll want to know who your competitor is. What do you know about this company and their products? Most important, what are your competitor’s strengths and weaknesses? Consider the interior design firm that is about to make a rebuy. If you’ve done your research, you might be able to tell the firm, “I know your current supplier offers a high-quality paint product in a wide range of colour choices. Our company offers a wide range of colour choices, too, and our product consistently gets high reviews. However, unlike your current provider, we also have a line of soy-based paints, which are better for the environment and for your customers’ and employees’ health than the regular latex variety. Using soy-based paints will increase your reputation as a progressive, socially responsible business.” Knowing your prospect’s current supplier gives you the power to favorably position your product by highlighting the things that set you apart from the competition.
- Current pricing. If the information is available, find out what your prospect’s current supplier charges for their product or service. This information will give you the edge to competitively position your solution. If you charge less than your competitors, you can highlight your product as a cost- saving alternative. If your products cost more, you might consider offering a discount or other benefit to provide a better solution. On the other hand, if your products are more expensive because they’re of a higher quality, you should emphasize that fact. For example, soy-based paint is generally more expensive than latex paint, but depending on your customer’s needs, the extra cost might be worth the benefits of a healthier, “greener” product.
4. About the Contact Person
- Title and role in the company. This is basic and essential information to know. It will help you to personalize your communications and will give you a better sense of your business situation. What role does this person have in the buying decision? Are you dealing with an influencer in the organization? Does this contact person have the authority to make a buying decision, or is this person a gatekeeper, a person with whom you must talk in order to get to the decision maker?
- Professional background. How long has this person been at the company, and what positions have they held? What roles have they had at other companies? This information will help you to adapt your communications and solutions to the individual. You can find valuable information on professional social networks such as LinkedIn and Twitter and use it as you prepare your approach and presentation. For instance, you might find out that someone in your network knows the person you are planning to approach and they can provide an entry for you. You might also learn that the person you plan on calling on was previously a buyer at two other companies and usually likes to bring in their previous vendors. If that’s the case, you might adapt your approach to include benefits that you have brought to other buyers who switched to your company.
- Personal information. Everyone likes to do business with people they like. Learning what you can about your contact’s family, hobbies, and interests demonstrates that you care about them as an individual and helps you build a relationship with your customer. This is useful information to keep on hand for the opening of the sales call when you want to put your prospect at ease and convince them of your goodwill. And its good information to use as follow-up or just to keep in touch. (“I know you are a huge University of Florida fan so I thought you would enjoy this video of the team’s summer training camp.”)
- Essential problem(s) your contact needs to solve. Knowing this information takes you right to the heart of the issue. Maybe your prospect is the marketing manager at the company and has recently been given the task of finding a new breakthrough idea for a promotional product to give away at a major upcoming industry trade show. Or maybe your prospect owns a grocery chain and needs to increase their sales in the frozen food area with organic products. Learning the specific problems your contact faces in their role at the company is the only way you can adapt your solution to meet their needs. The best way to identify your prospect’s problem (or opportunity) is to do extensive research on the company.
- Motivation for buying. If your contact is already buying from another supplier, what reasons might they have to start buying from you instead? For instance, are they dissatisfied with the quality of their current provider’s service or the price of the product? If they are satisfied, what value can you bring that provides a reason for them to consider changing suppliers? On the other hand, if this is a first-time purchase, what will drive their initial decision to buy?
5. About Your Existing Customers
Your current customers are your best prospects. While you might be excited about a new account, make sure you don’t spend so much time and energy on new prospects that you neglect the ones with whom you’ve already established a relationship.
- Opportunities to expand the relationship. There is no better place to increase your sales than with your existing customers. They know you and your product or service, you know them and their needs and challenges. So start by leveraging the information you already know about your customer’s business. This is the best way to expand your relationship. For instance, if you have sold fitness equipment to a regional chain of health clubs and you know that it is important for them to minimize maintenance costs and down time, you could target the buyer as a prospect for the new line of weight machines with hydraulics. You could also expand your research and determine how much money the club could save in a year based on the number of machines and include that as part of your presentation. This is establishing your value proposition, what you have to offer that your prospect or customer is willing to pay for. If your customer is using some of your services in combination with your competitor’s services, this is also a sales opportunity: find out how satisfied your customer is with the competitor’s services and see if you can come up with a better solution. (“You’re currently using our hydraulic weight machines, but I see that you’re buying your exercise machines from this other company. Did you know that we offer treadmills, exercise bikes, and elliptical machines that come with free maintenance and product replacement guarantees?”) If your customer has a contract with this competitor, finding out when the contract expires will help you time your sales call effectively.[5]
- Opportunities for synergy. How can you partner with your customer in new ways that will benefit both companies? Or are there additional services or products you offer that, used in combination with your customer’s current purchases, would create an even stronger solution? For example, Linksys has its Linksys One program, which offers B2B customers high-speed wireless networks combined with an Internet telephone service and several software services. By combining one company’s software and hardware products and services, customers are able to streamline their work, creating a simpler, more efficient system (Noronha, 2007). If you can demonstrate potential synergy with an existing customer—that is, collaboration that produces greater results than individual products, services, or parties could produce alone—you have an opportunity to expand your business with that customer.
6. Sources of Information
When you want to dig deeper with your research, you can often return to the same sources you used during the qualifying process and simply get more specific with the information you gather.
- Online searches for demographics of the key people in the organization.
- Business directories. Remember the library for paid subscriptions.
- Publicly available contracts. Real estate closings, government contracts, and other vital information that is part of public records can help provide pricing, terms, and other important data that can help you benchmark against the competition and better understand your prospect’s current situation.
- Trade journals. Trade journals are a good source for learning more about people and companies in your target industry.
- Blogs, social networks, and online forums. These online resources can provide insight about the prospect, the competition, and the environment. Many company employees and executives post regularly about their perceptions and feelings on many topics. These comments can provide valuable insight about the prospect.
- Professional organizations. Joining professional organizations (in person and online) can help you build relationships with contacts at your target companies. These organizations also serve as a source for competitive knowledge and for your connection to industry buzz.
In addition to these sources you’ve already used, consider another powerful resource: people. If you’ve already formed a relationship with key people in your target company, you can ask them for referrals to influencers in other departments of the organization. If they’re satisfied with the service you’ve been providing, these contacts are often happy to give you the names of others who might be able to use your solutions. Complementary salespeople can also be an excellent source of information about a prospect. For example, if you are selling computer hardware you might find nuggets of information from the person who sells office furniture. You can help each other by sharing insights and information.
It might surprise you to know that competitive salespeople can also be a resource. If you’re a member of a professional organization, if you attend conferences or tradeshows, or if you’re simply connected in your community, you’ll probably know competitive salespeople. While your competitor isn’t going to give you the inside scoop on a prospect they are currently pursuing, they might share some useful insights about companies or people they have worked with in the past.
- Rakham, N. (1996). The SPIN selling fieldbook. McGraw-Hill. ↵
- Capon, N. (2001). Key account management and planning. Free Press. ↵
- Tabio, G. (2009, May 14). Creative solutions. Presentation at Greater Media Philadelphia Sales Meeting, Philadelphia, PA. ↵
- Kamau, N. (2016, September 20). Successful strategic alliances: 5 examples of companies doing it right. Medium. https://medium.com/partner-sales-acceleration/successful-strategic-alliances-5-examples-of-companies-doing-it-right-5ef859c821c4 ↵
- Sim, M. (2008, August 12). Leveraging your CRM System to expand your client relationships. Get Entrepreneurial. http://www.getentrepreneurial.com/customer-service/leveraging_your_crm_system_to_expand_your_client_relationships.html ↵

