6 Child Maltreatment
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Define the four types of child maltreatment (physical abuse, emotional abuse, sexual abuse, and neglect).
- Identify risk factors for child maltreatment.
- Discuss protective factors and prevention strategies.
- List signs of each type of maltreatment.
- Explain what mandated reporting is and who it applies to.
Mandated Reporting
If you work with children in a family child care home or licensed child care facility, you are legally required or mandated to report and cannot shift the responsibility of reporting to your supervisor or to anyone else at your licensed facility. If you know or have reason to believe a child is being or has been neglected or physically or sexually abused within the preceding three years you must immediately (within 24 hours) make a report to an outside agency.
Introduction
One more responsibility early childhood educators have to protect children’s safety is to understand what child maltreatment is, the risk factors for child maltreatment, signs of different forms of child maltreatment, and what they should do to support children and families and what they must legally do if they suspect child maltreatment.
Looking at the Data
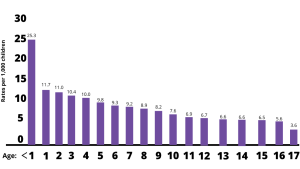
In 2017, there were 674,000 substantiated victims of child abuse and neglect across the U.S. The youngest children are the most vulnerable to maltreatment. Nationally, states report that more than one-quarter (28.5%) of victims are younger than 3 years old. The victimization rate is highest for children younger than 1-year-old at 25.3 per 1,000 children.
The percentages of child victims are similar for both boys (48.6%) and girls (51.0%). Sixty-nine percent of victims are maltreated by a mother, either acting alone (40.8%) or with a father and/or nonparent (28.2%). More than 13.0 percent (13.5%) of victims are maltreated by a perpetrator who was not the child’s parent. The largest categories in the nonparent group are relative (4.7%), partner of parent (2.9%), and “other” (2.7%).
The effects of child abuse and neglect are serious, and a child fatality is the most tragic consequence. In 2017, a national estimate of 1,720 children died from abuse and neglect at a rate of 2.32 per 100,000 children in the population.[2]
Definitions
Child maltreatment includes all types of abuse and neglect of a child under the age of 18 by a parent, caregiver, or another person in a custodial role (such as clergy, a coach, a teacher) that results in harm, potential for harm, or threat of harm to a child. There are four common types of abuse and neglect: physical abuse, sexual abuse, emotional abuse, and neglect. [1]
Physical Abuse
Physical abuse is a non-accidental physical injury to a child caused by a parent, caregiver, or other person responsible for a child and can include punching, beating, kicking, biting, shaking, throwing, stabbing, choking, hitting (with a hand, stick, strap, or other object), burning, or otherwise causing physical harm. Physical discipline, such as spanking or paddling, is not considered abuse as long as it is reasonable and causes no bodily injury to the child. Injuries from physical abuse could range from minor bruises to severe fractures or death.
Abusive Head Trauma
Abusive head trauma (AHT), which includes shaken baby syndrome, is a preventable and severe form of physical child abuse that results in an injury to the brain of a child. AHT is most common in children under age five, with children under one year of age at most risk. It is caused by violent shaking and/or with blunt impact. The resulting injury can cause bleeding around the brain or on the inside back layer of the eyes.Nearly all victims of AHT suffer serious, long-term health consequences such as vision problems, developmental delays, physical disabilities, and hearing loss. At least one of every four babies who experience AHT dies from this form of child abuse.
AHT often happens when a parent or caregiver becomes angry or frustrated because of a child’s crying. The caregiver then shakes the child and/or hits or slams the child’s head into something in an effort to stop the crying.Crying, including long bouts of inconsolable crying, is normal behaviour in infants. Shaking, throwing, hitting, or hurting a baby is never the right response to crying.How Can Abusive Head Trauma Be Prevented?Anyone can play a role in preventing AHT by understanding the dangers of violently shaking or hitting a baby’s head into something, knowing the risk factors and the triggers for abuse, and finding ways to support families and caregivers in their community.[5]
The Bottom Line
Shaking a baby can cause death or permanent brain damage. It can result in life-long disability. Healthy strategies for dealing with a crying baby include:
- finding the reason for the crying
- checking for signs of illness or discomfort, such as diaper rash, teething, tight clothing
- feeding or burping
- soothing the baby by rubbing its back; gently rocking; offering a pacifier; singing or talking;
- taking a walk using a stroller or a drive in a properly-secured car seat
- or calling the doctor if sickness is suspected.
All Babies Cry
Caregivers often feel overwhelmed by a crying baby. Calling a friend, relative, or neighbor for support or assistance lets the caregiver take a break from the situation. If immediate support is not available, the caregiver could place the baby in a crib (making sure the baby is safe), close the door, and check on the baby every five minutes.[6]
If an early childhood educator is growing frustrated with a child’s crying or other behaviours, it’s important that they follow the same advice they would give a parent/caregiver or find a co-worker to relieve them while they calm down.
Sexual Abuse
Child sexual abuse is a significant but preventable adverse childhood experience and public health problem. Sexual abuse includes activities by a parent or other caregiver such as fondling a child’s genitals, penetration, incest, rape, sodomy, indecent exposure, and exploitation through prostitution or the production of pornographic materials. Sexual abuse is defined by the Federal Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act as “the employment, use, persuasion, inducement, enticement, or coercion of any child to engage in, or assist any other person to engage in, any sexually explicit conduct or simulation of such conduct for the purpose of producing a visual depiction of such conduct; or the rape, and in cases of caretaker or interfamilial relationships, statutory rape, molestation, prostitution, or other form of sexual exploitation of children, or incest with children”[3]
About 1 in 4 girls and 1 in 13 boys experience child sexual abuse at some point in childhood. And 90% of child sexual abuse is perpetrated by someone the child or child’s family knows.[8]
Emotional Abuse
Emotional abuse (or psychological abuse) is a pattern of behaviour that impairs a child’s emotional development or sense of self-worth. This may include constant criticism, threats, or rejection as well as withholding love, support, or guidance. Emotional abuse is often difficult to prove, and, therefore, child protective services may not be able to intervene without evidence of harm or mental injury to the child (Prevent Child Abuse America, 2016). [4]
Neglect
Neglect is the failure of a parent or other caregiver to provide for a child’s basic needs. Neglect generally includes the following categories:
- Physical (e.g., failure to provide necessary food or shelter, lack of appropriate supervision).
- Medical (e.g., failure to provide necessary medical or mental health treatment, withholding medically indicated treatment from children with life-threatening conditions).
- Educational (e.g., failure to educate a child or attend to special education needs).
- Emotional (e.g., inattention to a child’s emotional needs, failure to provide psychological care, permitting a child to use alcohol or other drugs).

Sometimes cultural values, the standards of care in the community, and poverty may contribute to what is perceived as maltreatment, indicating the family may need information or assistance. It is important to note that living in poverty is not considered child abuse or neglect. However, a family’s failure to use available information and resources to care for their child may put the child’s health or safety at risk, and child welfare intervention could be required. In addition, many states provide an exception to the definition of neglect for parents/caregivers who choose not to seek medical care for their children due to religious beliefs.
Abandonment is considered in many states as a form of neglect. In general, a child is considered to be abandoned when the parent’s identity or whereabouts are unknown, the child has been left alone in circumstances where the child suffers serious harm, the child has been deserted with no regard for his or her health or safety, or the parent has failed to maintain contact with the child or provide reasonable support for a specified period of time. Some states have enacted laws—often called safe haven laws—that provide safe places for parents to relinquish newborn infants.
Pause to Reflect
- Come up with a situation that would be an example of each type of abuse and each type of neglect.
- Keep these in mind to revisit in another Pause to Reflect feature later in the chapter.
Risk Factors
Risk factors are those characteristics linked with child abuse and neglect—they may or may not be direct causes. A combination of individual, relational, community and societal factors contribute to the risk of child abuse and neglect. Although children are not responsible for the harm inflicted upon them, certain characteristics have been found to increase their risk of being abused and or neglected.
Individual Risk Factors for Victimization
- Children younger than 4 years of age.
- Special needs that may increase caregiver burden (e.g., disabilities, mental health issues, and chronic physical illnesses).
Risk Factors for Perpetration
There are different levels of risk factors for the perpetrators of child maltreatment
Individual Risk Factors
- Families’ lack of understanding of children’s needs, child development and parenting skills.
- Parental history of child abuse and or neglect.
- Substance abuse and/or mental health issues including depression in the family.
- Parental characteristics such as young age, low education, single parenthood, a large number of dependent children, and low income.
- Non-biological, transient caregivers in the home (e.g., mother’s male partner).
- Parental thoughts and emotions that tend to support or justify maltreatment behaviours.
Family Risk Factors
-

Figure 6.4 – Intimate partner violence is a family risk factor for child maltreatment. [11] Social isolation.
- Family disorganization, dissolution, and violence, including intimate partner violence.
- Parenting stress, poor parent-child relationships, and negative interactions.
Community Risk Factors
- Community violence.
- Concentrated neighborhood disadvantage (e.g., high poverty and residential instability, high unemployment rates, and high density of alcohol outlets), and poor social connections. [6]
Protective Factors
Protective factors may lessen the likelihood of children being abused or neglected. Protective factors have not been studied as extensively or rigorously as risk factors. Identifying and understanding protective factors are equally as important as researching risk factors.
Family Protective Factors
- Supportive family environment and social networks
- Concrete support for basic needs
- Nurturing parenting skills
- Stable family relationships
- Household rules and child monitoring
- Parental employment
- Parental education
- Adequate housing
- Access to health care and social services
- Caring adults outside the family who can serve as role models or mentors.
Community Protective Factors
Communities that support families and take responsibility for preventing abuse [7]
Preventative Strategies
Child abuse and neglect are serious problems that can have lasting harmful effects on its victims. The goal in preventing child abuse and neglect is to stop this violence from happening in the first place.
Child abuse and neglect are complex problems rooted in unhealthy relationships and environments. Preventing child abuse and neglect requires addressing factors at all levels of the social ecology–the individual, relational, community, and societal levels. [8]As you can see in Figure 6.5, early care and education has a direct role to play in one of the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Violence Prevention’s strategies and can support families in some of the others. Families who have access to quality childcare, which increases the likelihood that children will experience safe, stable, nurturing relationships and environments. Access to affordable childcare also reduces parental stress and maternal depression, which are risk factors for child abuse and neglect.[15]

Domestic Violence
Given the magnitude of the problem of children’s exposure to violence, including the co-occurrence of domestic violence and child maltreatment, early care and education programs are serving children and families impacted by violence. Here are some key facts about domestic violence and intimate partner violence:
- Intimate partner violence describes physical, sexual, or psychological harm by a current or former partner or spouse. This type of violence can occur among heterosexual or same-sex couples and does not require sexual intimacy. Intimate partner violence can vary in frequency and severity. It occurs on a continuum ranging from one hit that may or may not impact the victim to chronic, severe beating.
- Domestic violence is the second leading cause of death for pregnant women, and some 25 to 50 percent of adolescent mothers experience partner violence before, during, or just after their pregnancy.
- Witnessing family assault is among the most common victimizations experienced by toddlers (ages 2 to 5). Other common forms of victimization are assault by a sibling and physical bullying.
- In 30 to 60 percent of families where either child abuse or domestic violence is present, child abuse and domestic violence co-occur.
Children may very well experience the violence themselves; however, even when they are not directly injured, exposure to traumatic events can cause social, emotional, and behavioural difficulties. Children exposed to domestic violence have often been found to develop a wide range of problems, including externalizing behaviour problems, interpersonal skill deficits, and psychological and emotional problems such as depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). In addition, a Michigan study of preschool-aged children found that those exposed to domestic violence at home are more likely to have health problems, including allergies, asthma, frequent headaches and stomach-aches, and generalized lethargy.
What Early Care and Education Programs Should Do to Help
It is critical that early childhood educators be prepared to work with and guide these children and families to needed services. Teachers and administrators can support the child and family during times of stress by making hotline and other domestic violence information available to families.
The early childhood workforce is currently comprised of about 1 million center-based teachers and caregivers, 1 million home-based teachers and caregivers, and an additional 2.7 million unpaid home-based teachers and caregivers. This workforce consists largely of women, and women are disproportionately affected by domestic violence. Therefore, information about appropriate services and programs should be made available for both staff and families. [10]
Signs of Child Maltreatment
It is important to recognize high-risk situations and the signs and symptoms of maltreatment. If you suspect a child is being harmed or the child directly discloses that they have experienced abuse or neglect, reporting suspicions may protect him or her and help the family receive assistance. Any concerned person can report suspicions of child abuse or neglect. Reporting your concerns is not making an accusation; rather, it is a request for an investigation and assessment to determine if help is needed.
| Table 6.1 – Signs of General Maltreatment [11] | |
| Child | Shows sudden changes in behaviour or school performance. Has not received help for physical or medical problems brought to the families’ attention. Has learning problems (or difficulty concentrating) that cannot be attributed to specific physical or psychological causes. Is always watchful, as though preparing for something bad to happen.Lacks adult supervision. Is overly compliant, passive, or withdrawn. Comes to school or other activities early, stays late, and does not want to go home. Is reluctant to be around a particular person. Discloses maltreatment. |
| Parent/caregiver | Denies the existence of—or blames the child for—the child’s problems in school or at home. Asks teachers or other caregivers to use harsh physical discipline if the child misbehaves. Sees the child as entirely bad, worthless, or burdensome. Demands a level of physical or academic performance the child cannot achieve. Looks primarily to the child for care, attention, and satisfaction of the parent’s emotional needs. Shows little concern for the child. |
| Parent/caregiver and child | Touch or look at each other rarely. Consider their relationship entirely negative. State consistently they do not like each other. |

It is important to pay attention to other behaviours that may seem unusual or concerning. Additionally, the presence of these signs does not necessarily mean that a child is being maltreated; there may be other causes. They are, however, indicators that others should be concerned about the child’s welfare, particularly when multiple signs are present or they occur repeatedly.
Signs of Specific Forms of Child Maltreatment
| Table 6.2 – Signs of Physical Abuse [12] | |
| Scenario | Characteristics |
| A child who exhibits the following signs may be a victim of physical abuse: | Has unexplained injuries, such as burns, bites, bruises, broken bones, or black eyes. Has fading bruises or other noticeable marks after an absence from school. Seems scared, anxious, depressed, withdrawn, or aggressive. Seems frightened of his or her parents/caregivers and protests or cries when it is time to go home. Shrinks at the approach of adults. Shows changes in eating and sleeping habits. Reports injury by a parent or another adult caregiver. Abuses animals or pets. |
| Consider the possibility of physical abuse when a parent or other adult caregiver exhibits the following | Offers conflicting, unconvincing, or no explanation for the child’s injury or provides an explanation that is not consistent with the injury. Shows little concern for the child. Sees the child as entirely bad, burdensome, or worthless. Uses harsh physical discipline with the child. Has a history of abusing animals or pets. |
| Table 6.3 – Signs of Sexual Abuse [13] | |
| Scenario | Characteristics |
| A child who exhibits the following signs may be a victim of sexual abuse: | Has difficulty walking or sitting. Experiences bleeding, bruising, or swelling in their private parts. Suddenly refuses to go to school. Reports nightmares or bedwetting. Experiences a sudden change in appetite. Demonstrates bizarre, sophisticated, or unusual sexual knowledge or behaviour. Becomes pregnant or contracts a sexually transmitted disease, particularly if under age 14. Runs away. Reports sexual abuse by a parent or another adult caregiver. Attaches very quickly to strangers or new adults in their environment. |
| Consider the possibility of sexual abuse when a parent or other adult caregiver exhibits the following | Tries to be the child’s friend rather than assume an adult role. Makes up excuses to be alone with the child. Talks with the child about the adult’s personal problems or relationships. |
| Table 6.4 –Signs of Emotional Abuse [14] | |
| Scenario | Characteristics |
| A child who exhibits the following signs may be a victim of emotional abuse: | Shows extremes in behaviour, such as being overly compliant or demanding, extremely passive, or aggressive. Is either inappropriately adult (e.g., parenting other children) or inappropriately infantile (e.g., frequently rocking or head-banging). Is delayed in physical or emotional development. Shows signs of depression or suicidal thoughts. Reports an inability to develop emotional bonds with others. |
| Consider the possibility of emotional abuse when a parent or other adult caregiver exhibits the following | Constantly blames, belittles, or berates the child. Describes the child negatively. Overtly rejects the child. |
| Table 6.5 – Signs of Neglect [15] | |
| Scenario | Characteristics |
| A child who exhibits the following signs may be a victim of neglect: | Is frequently absent from school. Begs or steals food or money. Lacks needed medical care (including immunizations), dental care, or glasses. Is consistently dirty and has severe body odor. Lacks sufficient clothing for the weather. Abuses alcohol or other drugs. States that there is no one at home to provide care. |
| Consider the possibility of neglect when a parent or other adult caregiver exhibits the following | Appears to be indifferent to the child. Seems apathetic or depressed. Behaves irrationally or in a bizarre manner. Abuses alcohol or other drugs. |
Pause to Reflect
Think back to your example situations.
- What signs might a teacher or caregiver notice for each of these?
Mandated Reporting of Child Maltreatment
A list of persons whose profession qualifies them as “mandated reporters” of child abuse or neglect includes professionals and their delegates in the following fields:
- Health Care
- Social Services (social workers, group home staff, foster parents)
- Mental Health Services (psychiatrists, psychologists, therapists)
- Child Care (family child care and center child care programs)
- Education (all teachers, administrators, support staff and other school personnel)
- Law enforcement, probation and correctional services
- Guardian ad litem
- Clergy (exempt in certain circumstances).

All persons who are mandated reporters are required, by law, to report all known or suspected cases of child abuse or neglect. It is not the job of the mandated reporter to determine whether the allegations are valid. If child abuse or neglect is reasonably suspected or if the child shares information with a mandated reporter leading him/her to believe abuse or neglect has taken place, the report must be made. No supervisor or administrator can impede or inhibit a report or subject the reporting person to any sanction.
To make a report, an employee must contact appropriate local law enforcement or county child welfare agency, listed below. This legal obligation is not satisfied by making a report of the incident to a supervisor or to the school. An appropriate law enforcement agency may be one of the following:
- A Police or Sheriff’s Department (not including a school district police department or school security department).
- A County Probation Department, if designated by the county to receive child abuse reports.
- A County Welfare Department/County Child Protective Services.
The report should be made immediately over the telephone and should be followed up in writing. The law enforcement agency has special forms for this purpose that they will ask you to complete. If a report cannot be made immediately over the telephone, then an initial report may be made via e-mail or fax.
Rights to Confidentiality and Immunity
Mandated reporters are required to give their names when making a report. However, the reporter’s identity is kept confidential. Reports of suspected child abuse are also confidential. Mandated reporters have immunity from state criminal or civil liability for reporting as required. This is true even if the mandated reporter acquired the knowledge, or suspicion of abuse or neglect, outside his/her professional capacity or scope of employment.
Consequences of Failing to Report
A person who fails to make a required report is guilty of a misdemeanor.
After the Report is Made
The local law enforcement agency is required to investigate all reports. Cases may also be investigated by Child Protective Services when allegations involve abuse or neglect within families.
Child Protective Services
Child Protective Services (CPS) is the major organization to intervene in child abuse and neglect cases in Minnesota. Existing law provides services to abused and neglected children and their families. More information can be found at Child Protective Services. [17]
The Impact of Childhood Trauma on Well-Being
Child abuse and neglect can have lifelong implications for victims, including on their wellbeing. While the physical wounds may heal, there are many long-term consequences of experiencing the trauma of abuse or neglect. A child or youth’s ability to cope and thrive after trauma is called “resilience.” With help, many of these children can work through and overcome their past experiences.
Children who are maltreated may be at risk of experiencing cognitive delays and emotional difficulties, among other issues, which can affect many aspects of their lives, including their academic outcomes and social skills development (Bick & Nelson, 2016). Experiencing childhood maltreatment also is a risk factor for depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric disorders (FullerThomson, Baird, Dhrodia, & Brennenstuhl, 2016). [18]
We will look more closely at this when we examine mental health, social and emotional well-being, adverse childhood events, and trauma informed care in Chapter 11.
Working with Children that Have Been Abused
Children who have experienced abuse or neglect need support from caring adults who understand the impact of trauma and how to help. Adverse childhood experiences and trauma-informed care will be addressed more in Chapter 11. Early childhood educators should consider the following suggestions:
- Help children feel safe. Support them in expressing and managing intense emotions.
- Help children understand their trauma history and current experiences (for example, by helping them understand that what happened was not their fault, or helping them see how their current emotions might be related to past trauma).
- Assess the impact of trauma on the child, and address any trauma-related challenges in the child’s behaviour, development, and relationships.
- Support and promote safe and stable relationships in the child’s life, including supporting the child’s family and caregivers if appropriate. Often parents and caregivers have also experienced trauma.
- Manage your own stress. Providers who have histories of trauma themselves may be at particular risk of experiencing secondary trauma symptoms.
- Refer the child to trauma-informed services, which may be more effective than generic services that do not address trauma.[27]
Summary
Child maltreatment results from the interaction of a number of individual, family, societal, and environmental factors. Child abuse and neglect are not inevitable—safe, stable, and nurturing relationships and environments are key for prevention. Preventing child abuse and neglect can also prevent other forms of violence, as various types of violence are interrelated and share many risk and protective factors, consequences, and effective prevention tactics. [19]When there is suspicion that maltreatment has occurred, it’s critical that early childhood educators report that. And being educated on trauma-informed care can help you support children who have been the victims of child maltreatment.
Chapter 6 Review
Resources for Further Exploration
- What is Child Abuse and Neglect?
- Children’s Bureau
- Children’s Bureau’s Office on Child Abuse and Neglect Prevention Guide
- Center for Disease Control
- Resource Guide for Mandated Reporters
- National Center on Shaken Baby Syndrome
- American Professional Society on the Abuse of Children
- Child Welfare League of America (CWLA)
- Prevent Child Abuse America
References:
[1] Child Maltreatment 2017 by the Administration for Children and Families is in the public domain.
[2] Child Maltreatment 2017 by the Administration for Children and Families is in the public domain.
[11] Shining a light on domestic violence by Airman 1st Class Destinee Sweeney is in the public domain.
[15] Preventing Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs): Leveraging the Best Available Evidence by the CDC is in the public domain.
[20] More than meets the eye by Airman 1st Class Jessica H. Smith is in the public domain.
[27] 2018 Prevention Resource Guide by the Administration for Children and Families is in the public domain.
- CDC. (2022). What are child abuse and neglect? [public domain]. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/childabuseandneglect/fastfact.html ↵
- Image by the U.S. Air Force is in the public domain ↵
- Children's Bureau. (2019). What is Child Abuse and Neglect? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms. [public domain]. https://cwig-prod-prod-drupal-s3fs-us-east-1.s3.amazonaws.com/public/documents/whatiscan.pdf ↵
- Children's Bureau. (2019). What is Child Abuse and Neglect? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms. [public domain]. https://cwig-prod-prod-drupal-s3fs-us-east-1.s3.amazonaws.com/public/documents/whatiscan.pdf ↵
- Safe Surrender Site San Francisco Fire Station14 by Alexander Klink is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- CDC. (2022). Risk and Protective Factors. [public domain].https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/childabuseandneglect/riskprotectivefactors.html ↵
- CDC. (2022). Risk and Protective Factors. [public domain].https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/childabuseandneglect/riskprotectivefactors.html ↵
- CDC. (2022). Prevention Strategies. [public domain] https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/childabuseandneglect/prevention.html. ↵
- CDC. (2022). What are child abuse and neglect? [public domain]. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/childabuseandneglect/fastfact.html ↵
- Office of Head Start. (n.d.).Helping Children and Families Experiencing Domestic/Intimate Partner Violence ACF-IM-HS-14-06. [public domain]. https://eclkc.ohs.acf.hhs.gov/policy/im/acf-im-hs-14-06 ↵
- Children's Bureau. (2019). What is Child Abuse and Neglect? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms. [public domain]. https://cwig-prod-prod-drupal-s3fs-us-east-1.s3.amazonaws.com/public/documents/whatiscan.pdf ↵
- Children's Bureau. (2019). What is Child Abuse and Neglect? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms. [public domain]. https://cwig-prod-prod-drupal-s3fs-us-east-1.s3.amazonaws.com/public/documents/whatiscan.pdf ↵
- Children's Bureau. (2019). What is Child Abuse and Neglect? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms. [public domain]. https://cwig-prod-prod-drupal-s3fs-us-east-1.s3.amazonaws.com/public/documents/whatiscan.pdf ↵
- Children's Bureau. (2019). What is Child Abuse and Neglect? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms. [public domain]. https://cwig-prod-prod-drupal-s3fs-us-east-1.s3.amazonaws.com/public/documents/whatiscan.pdf ↵
- Children's Bureau. (2019). What is Child Abuse and Neglect? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms. [public domain]. https://cwig-prod-prod-drupal-s3fs-us-east-1.s3.amazonaws.com/public/documents/whatiscan.pdf ↵
- Image by Petr Kratochvil is in the public domain. ↵
- Minnesota Department of Human Services. (2016). Resource Guide for Mandated Reporters. https://www.dowr.org/img/Reporting%20Child%20Abuse%20and%20Neglect%201_16.pdf ↵
- Children's Bureau. (2019). What is Child Abuse and Neglect? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms. [public domain]. https://cwig-prod-prod-drupal-s3fs-us-east-1.s3.amazonaws.com/public/documents/whatiscan.pdf ↵
- CDC. (2022). What are child abuse and neglect? [public domain]. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/childabuseandneglect/fastfact.html ↵

