10.8 End-of-Chapter Material
Additional Exercises
-
Explain why iron and copper have the same Lewis electron dot diagram when they have different numbers of electrons.
-
Name two ions with the same Lewis electron dot diagram as the Cl− ion.
-
Based on the known trends, what ionic compound from the first column of the periodic table and the next-to-last column of the periodic table should have the highest lattice energy?
-
Based on the known trends, what ionic compound from the first column of the periodic table and the next-to-last column of the periodic table should have the lowest lattice energy?
-
P2 is not a stable form of phosphorus, but if it were, what would be its likely Lewis electron dot diagram?
-
Se2 is not a stable form of selenium, but if it were, what would be its likely Lewis electron dot diagram?
-
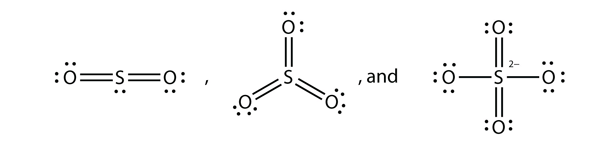
What are the Lewis electron dot diagrams of SO2, SO3, and SO42−?
-
What are the Lewis electron dot diagrams of PO33− and PO43−?
-
Which bond do you expect to be more polar—an O–H bond or an N–H bond?
-
Which bond do you expect to be more polar—an O–F bond or an S–O bond?
-
Use bond energies to estimate the energy change of this reaction.
C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O
-
Use bond energies to estimate the energy change of this reaction.
N2H4 + O2 → N2 + 2 H2O
-
Ethylene (C2H4) has two central atoms. Determine the geometry around each central atom and the shape of the overall molecule.
-
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) has two central atoms. Determine the geometry around each central atom and the shape of the overall molecule.
-
Determine the molecular dipole moments for the following molecules: