15.2 Reaction Rates
Learning Objectives
- To gain an understanding of relative reaction rates.
- To gain an understanding of instantaneous reaction rates and initial reaction rates.
We encounter rates or speeds often in daily life; for example, the rate at which this textbook was typed could be measured in words per minute. This rate is a measure of the change in words typed in the time period of a minute. Similarly, the rate of a chemical reaction is also a measure of change that occurs in a given time period:
Rate of reaction = (Change in Concentration)/(Change in Time)
For a chemical reaction, we can measure the change in concentration in terms of either the disappearance of starting material or the appearance of the product. For the hypothetical reaction: A + B → C, we can express the average rate of reaction as follows:
Rate of reaction = – ∆[A] / ∆t = – ∆[B] / ∆t = ∆[C] / ∆t
Notice that a negative sign is included when expressing reaction rates with respect to the disappearance of starting materials. Reaction rates are always positive, so the decrease in concentration must be corrected for.
When the stoichiometric relationships in the balanced equation are not 1:1, the coefficient for each species must also be corrected for. In the hypothetical reaction 2 A + B → 3 C, two molecules of A are consumed for every one molecule of B, this means A is consumed twice as fast. To correct for this and express the average rate of reaction for each species, we must divide each by its coefficient in the balanced equation:
Rate of reaction = – ½∆[A] / ∆t = – ∆[B] / ∆t = (1/3) ∆[C] / ∆t
Example 1
The decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) was performed in the lab and the rate of formation of NO2 was found to be 0.53 M/s.
1. What was the rate of formation of O2(g)?
2. What was the rate of consumption N2O5(g)?
Solution
a. First determine the rate relationship between NO2(g) and O2(g) using the coefficients of the balanced equation:
Rate of reaction = ¼ ∆[NO2]/∆t = ∆[O2]/∆t
Next substitute in the given values and solve for the rate of formation of O2(g):
Rate of formation of O2(g) = (1/4) (0.53 M/s) = 0.13 M/s
b. First determine the rate relationship between NO2(g) and N2O5(g) using the coefficients of the balanced equation:
Rate of reaction = ¼ ∆[NO2]/∆t = ½ ∆[N2O5]/∆t
Next substitute the given values and solve for the rate of consumption of N2O5(g):
-½ rate of consumption of N2O5(g) = -¼ rate of formation NO2(g)
Rate of consumption of N2O5(g) = ½ (0.53 M/s) = 0.27 M/s
Instantaneous Rate
For most chemical reactions, the rate of the reaction tends to decrease as time passes (Figure 15.6 “Reactant Concentration vs. Time“). As the reaction proceeds, more and more of the reactant molecules are consumed to become product, which lowers the concentration of reactant molecules. The reduction in reactant concentration results in fewer effective collisions.
The decrease in reaction rate over time means that average reaction rates do not accurately represent the actual rate of reaction at all time points. Instantaneous reaction rates, the rate of reaction at one instant in time, can be determined from the slope of the tangent at that point in the plot of concentration vs. time. The instantaneous rate at the start of the reaction, t = 0, is of particular interest in kinetics and is known as the initial rate of the reaction.
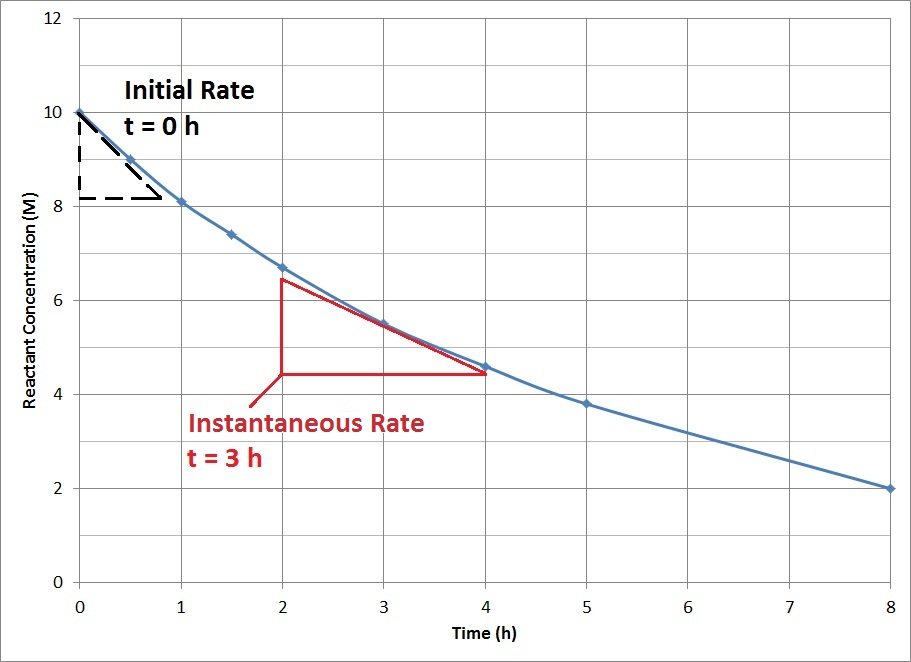
A plot of reactant concentration vs. time for a hypothetical reaction.
Example 2
Use Figure 15.6 to determine the instantaneous rate at 3 h.
Solution
The slope of the tangent at 3 h can be determined by drawing a triangle such as the one shown in Figure 15.6, and comparing the ratio of the height of the rise to the run of the length.
Slope = rise / run = – ∆[Reactant] / ∆t = – (4.5-6.5 M)/(4-2 h) = – (-2 M)/(2 h) = 1 M/h
Key Takeaways
- Reaction rates can be measured by the disappearance of starting material or the appearance of the product over time.
- Instantaneous reaction rates can be determined from the slope of the tangent at that point in the plot of concentration vs. time.
- The initial reaction rate is the instantaneous rate at the start of the reaction (at t = 0).

