4.5 Exercises
Analysis Problems
- For the amplifier of Figure 4.5.1 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝐴𝑣 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛 = 20 mV, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 10 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −2 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 20 V, 𝑅𝐺 = 750 k Ω , 𝑅𝐷 = 2 k Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 4 k Ω , 𝑅𝑆 = 1 k Ω , 𝑅𝑆𝑊 = 200 Ω .
- For the amplifier of Figure 4.5.1 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛 = 25 mV, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 15 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −2 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 22 V, 𝑅𝐺 = 330 k Ω , 𝑅𝐷 = 2 k Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 6 k Ω , 𝑅𝑆 = 510 Ω , 𝑅𝑆𝑊 = 220 Ω .
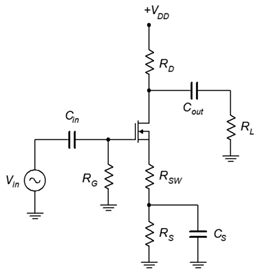
Figure 4.5.1 - For the circuit of Figure 4.5.2 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝐴𝑣 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛 = 10 mV, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 12 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −2.5 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 26 V, 𝑅𝐺 = 510 k Ω , 𝑅𝐷 = 1.2 k Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 25 k Ω .
- For the circuit of Figure 4.5.2 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛 = 25 mV, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 15 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −1.5 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 24 V, 𝑅𝐺 = 820 k Ω , 𝑅𝐷 = 1 k Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 12 k Ω .

Figure 4.5.2 - For the circuit of Figure 4.5.3 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛= 25 mV, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 8 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −3.5 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 24 V, 𝑅1 = 1 M Ω , 𝑅2 = 100 k Ω , 𝑅𝐷 = 800 Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 10 k Ω .
- For the circuit of Figure 4.5.3 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝐴𝑣 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛 = 10 mV, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 6 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −4 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 26 V, 𝑅1 = 2 M Ω , 𝑅2 = 120 k Ω , 𝑅𝐷 = 1.2 k Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 15 k Ω .
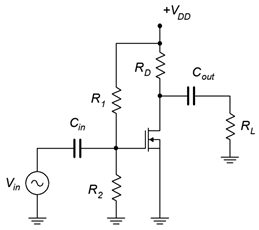
Figure 4.5.3 - For the circuit of Figure 4.5.4 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛 = 20 mV, 𝐼𝐷(𝑜𝑛) = 6 mA at 𝑉𝐷𝑆(𝑜𝑛) = 3 V, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑡ℎ) = 2.5 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 34 V, 𝑅1 = 1 M Ω , 𝑅2 = 100 k Ω , 𝑅𝐷 = 1 k Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 10 k Ω .
- For the circuit of Figure 4.5.4 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝐴𝑣 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛 = 15 mV, 𝐼𝐷(𝑜𝑛) = 10 mA at 𝑉𝐷𝑆(𝑜𝑛) = 4 V, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑡ℎ) = 2 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 30 V, 𝑅1 = 2 M Ω , 𝑅2 = 180 k Ω , 𝑅𝐷 = 1.2 k Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 15 k Ω .

Figure 4.5.4 - For the circuit of Figure 4.5.5 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛= 200 mV, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 15 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −3 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 15 V, 𝑅𝐺 = 910 k Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 10 k Ω , 𝑅𝑆 = 330 Ω .
- For the circuit of Figure 4.5.5 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 . 𝑉𝑖𝑛 = 200 mV, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 20 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −2 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 12 V, 𝑅𝐺 = 1 M Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 1.8 k Ω , 𝑅𝑆 = 220 Ω .
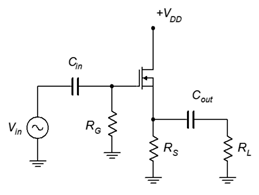
Figure 4.5.5 - For the circuit of Figure 4.5.6 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝐴𝑣 . 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 18 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −2 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 12 V, 𝑉𝑆𝑆 = −4 V, 𝑅𝐺 = 680 k Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 10 k Ω , 𝑅𝑆 = 1 k Ω .
- For the circuit of Figure 4.5.6 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝐴𝑣. 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 20 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −2 V, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 10 V, 𝑉𝑆𝑆 = −6 V, 𝑅𝐺 = 2.2 M Ω , 𝑅𝐿 = 5 k Ω , 𝑅𝑆 = 510 Ω .

Figure 4.5.6
Design Problems
- Following the circuit of Figure 4.5.1 , design an amplifier with a gain of at least 5 and an input impedance of at least 500 k Ω . 𝑅𝐿 = 10 k Ω . The MOSFET has the following parameters: 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −2 V, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 25 mA. Try to use standard resistor values.
- Using the circuit of Figure 4.5.5 , design a follower with a gain of at least .75 and an input impedance of at least 1 M Ω . 𝑅𝐿 = 2 k Ω . The MOSFET has the following parameters: 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −1.5 V, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 40 mA. Try to use standard resistor values.
Challenge Problems
- For the circuit of Figure 4.5.7 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝐴𝑣 . 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 15 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −2 V.

Figure 4.5.7 - For the circuit of Figure 4.5.8 , determine 𝑍𝑖𝑛 and 𝐴𝑣 . 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 12 mA, 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −1.5 V.

Figure 4.5.8
Computer Simulation Problems
- Utili 𝑍𝑖𝑛 g manufacturer’s data sheets, find devices with the following specifications (typical) and verify them using the measurement techniques presented in the prior chapter.
- Device 1: 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −2 V, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 25 mA.
- Device 2: 𝑉𝐺𝑆(𝑜𝑓𝑓) = −1.5 V, 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 = 40 mA.
- Using the device model from the preceding problem, verify the design of Problem 4.
- Using the device model from Problem 17, verify the design of Problem 14.

